Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Exp Med. May 20, 2015; 5(2): 40-49
Published online May 20, 2015. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v5.i2.40
Published online May 20, 2015. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v5.i2.40
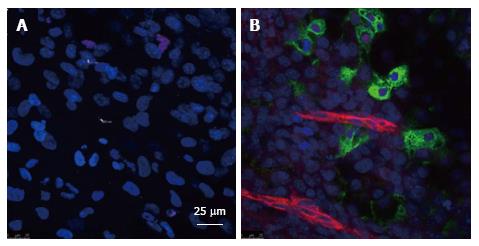
Figure 4 Analysis of blood vessels and insulin-producing cells in embryoid bodies obtained from human embryonic stem cell line H9.
Human embryonic stem cells were cultured in suspension for 5 d to obtain embryoid bodies (EB). After attachment on coverslips for 24 h. Some EBs were cultured alone or together with human microvascular endothelial cells (HMECs). Then, after 20 d both groups of EBs were fixed and stained with with anti-proinsulin (green) (a marker for pancreatic beta cells), anti-CD31 (red) (a marker for endothelial cells), and DAPI (blue) (that stains the nuclei). A: EB cells cultured alone that do not show proinsulin or CD31 expression. In contrast with (B) EB cells co-cultured with HMECs at passage 14 in which we can find cells that express proinsulin in close proximity to cells that express CD31. HMECs did not stain positive for CD31 at the dilutions used indicating that the ECs are forming within EBs.
- Citation: Talavera-Adame D, Dafoe DC. Endothelium-derived essential signals involved in pancreas organogenesis. World J Exp Med 2015; 5(2): 40-49
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v5/i2/40.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v5.i2.40