Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Exp Med. May 20, 2015; 5(2): 40-49
Published online May 20, 2015. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v5.i2.40
Published online May 20, 2015. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v5.i2.40
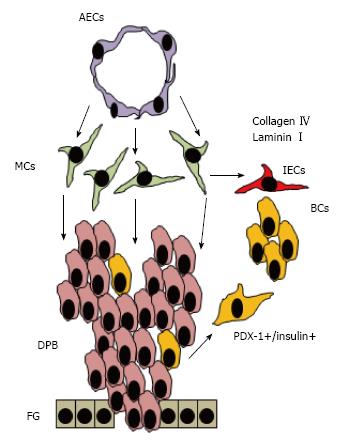
Figure 3 Endothelial-derived signals promote the survival of pancreatic mesenchyme which is essential for pancreas development.
Mesenchymal cells (MCs) appear between AECs and the dorsal pancreatic bud (DPB) and promote proliferation and survival of differentiated cells. Immature beta cells (BCs) that co-express PDX-1 and insulin migrate toward the mesenchyme and form cell clusters that will become islet of Langerhans that will recruit ECs that become islet ECs (iECs) and produce collagen IV and laminins which promote insulin expression. AECs crosstalk with MCs and maintain the integrity of these cells toward adequate exocrine and endocrine pancreas development. AECs: Aortic ECs; ECs: Endothelial cells; PDX: Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox.
- Citation: Talavera-Adame D, Dafoe DC. Endothelium-derived essential signals involved in pancreas organogenesis. World J Exp Med 2015; 5(2): 40-49
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v5/i2/40.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v5.i2.40