Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Exp Med. Nov 20, 2013; 3(4): 100-107
Published online Nov 20, 2013. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v3.i4.100
Published online Nov 20, 2013. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v3.i4.100
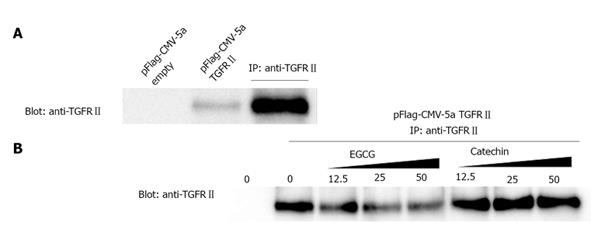
Figure 4 (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate interferes with binding between transforming growth factor-β and its type II receptor.
A: Positive control of the immunoprecipitation experiment. Cell lysates from transfected COS-7 cells were treated with anti-transforming growth factor-β type II receptor (TGFRII). TGFRII was recovered in the immunoprecipitation product of the lysate; B: Effects of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) and catechin on the antigen-antibody interaction. After cells were treated with EGCG or catechin, anti-TGFRII bound to Protein G was added to each lysate. Western blotting was performed using anti-TGFRII.
- Citation: Tabuchi M, Hayakawa S, Honda E, Ooshima K, Itoh T, Yoshida K, Park AM, Higashino H, Isemura M, Munakata H. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses transforming growth factor-beta signaling by interacting with the transforming growth factor-beta type II receptor. World J Exp Med 2013; 3(4): 100-107
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v3/i4/100.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v3.i4.100