Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Exp Med. Nov 20, 2013; 3(4): 100-107
Published online Nov 20, 2013. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v3.i4.100
Published online Nov 20, 2013. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v3.i4.100
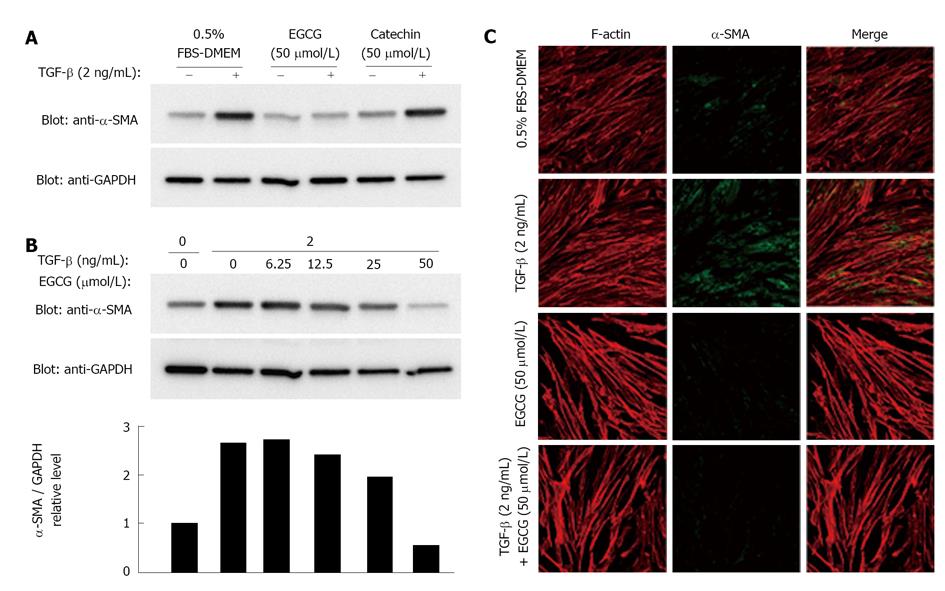
Figure 1 Effects of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on expression of α-smooth muscle actin.
A: Lysates of MRC-5 cells were obtained from cells treated with 0.5% FBS in DMEM alone, (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) (50 μmol/L), or catechin (50 μmol/L) for 24 h. After SDS-PAGE, proteins were blotted onto Immobilon, and probed with anti-α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) antibody. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as an internal control; B: MRC-5 cells were treated with the indicated amounts of EGCG. α-SMA was detected in the same manner as in (A). The expression levels of α-SMA were normalized to those of GAPDH; C: Expression of α-SMA in cells treated with EGCG (50 μmol/L) in the absence (-) or presence (+) of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) (2 ng/mL) were examined by confocal microscopy. Green: α-SMA (fluorescein isothiocyanate conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG); Red: Actin stress fiber (rhodamine-labeled phalloidin); blue: Nuclei (DAPI). FBS: fetal bovine serum.
- Citation: Tabuchi M, Hayakawa S, Honda E, Ooshima K, Itoh T, Yoshida K, Park AM, Higashino H, Isemura M, Munakata H. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses transforming growth factor-beta signaling by interacting with the transforming growth factor-beta type II receptor. World J Exp Med 2013; 3(4): 100-107
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v3/i4/100.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v3.i4.100