Copyright
©2012 Baishideng.
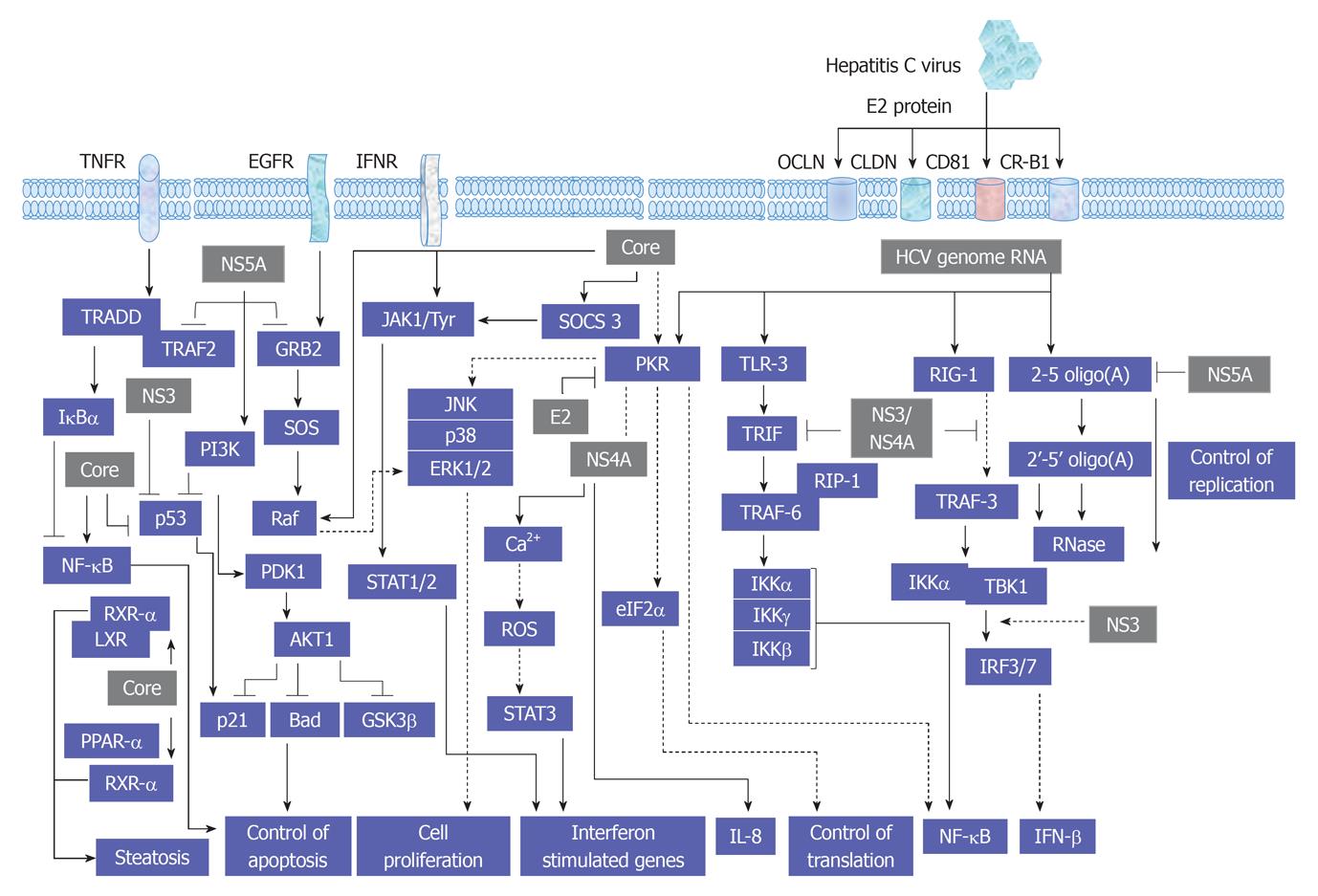
Figure 2 A proposed model for the consequences resulting from the interference of hepatitis C virus with signal transduction processes in host cells.
HCV: Hepatitis C virus; TNFR: Tumor necrosis factor receptor; JAK: Janus kinase; EGFR: Endothelial growth factor receptor; IFN: Interferon; IFNR: IFN receptor; TRAF: Tumor necrosis factor associated factor; TRADD: TNFR-associated protein with death domain; JAK: Janus kinase; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; SOCS: Suppressor of cytokine signaling; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; ERK: Extracellular regulated protein kinase; RIP: Receptor-interacting protein; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; STAT: Signal transducers and activators of transcription; NF-κB: Nuclear factor κB; IL: Interleukin; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor.
- Citation: Hassan M, Selimovic D, El-Khattouti A, Ghozlan H, Haikel Y, Abdelkader O. Hepatitis C virus-host interactions: Etiopathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. World J Exp Med 2012; 2(2): 7-25
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v2/i2/7.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v2.i2.7