Copyright
©2012 Baishideng.
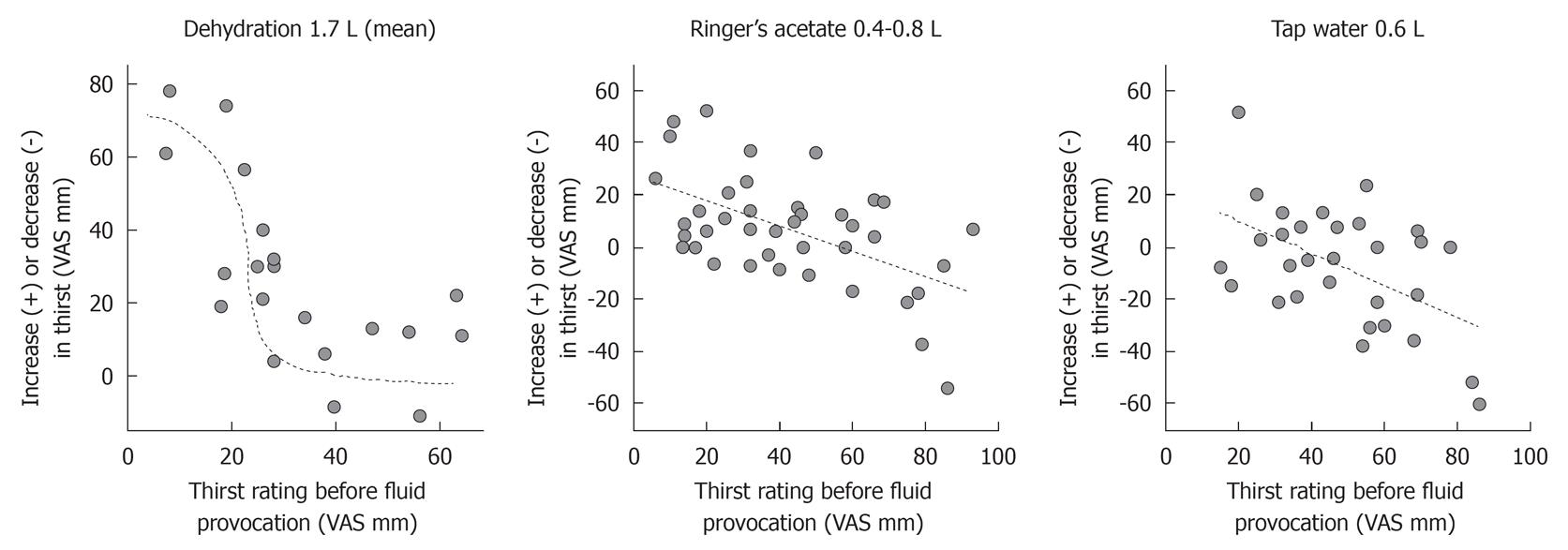
Figure 2 Volume depletion by furosemide increased thirst only in volunteers who were thirsty before volume depletion was initiated (left); conversely, intravenous infusion of Ringer’s acetate solution (middle) and ingestion of tap water (right) decreased thirst only in those who were thirsty before the respective provocation (challenge) of the fluid balance.
- Citation: Li YH, Waldréus N, Zdolsek J, Hahn RG. Effects of tap water, electrolyte solution, and spontaneous and furosemide-stimulated urinary excretion on thirst. World J Exp Med 2012; 2(1): 1-6
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v2/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v2.i1.1