Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Crit Care Med. May 4, 2017; 6(2): 107-115
Published online May 4, 2017. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v6.i2.107
Published online May 4, 2017. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v6.i2.107
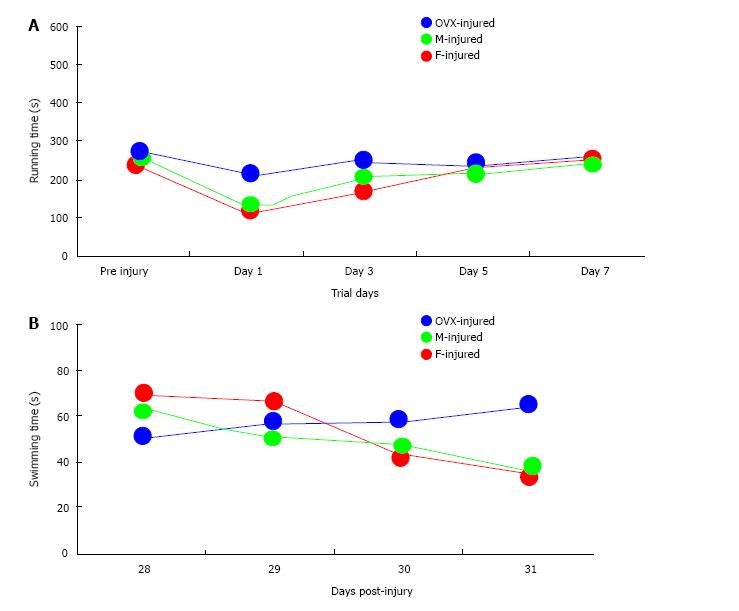
Figure 2 Short- and long-term neurobehavioral measurements after mild traumatic injury in mice.
Rotarod latencies (A) were not different over Days 1-7 after moderate traumatic brain injury (MTBI) (P = 0.62; ANOVA). Significant water maze (WM) latencies (B) differences were demonstrated between groups over Days 28-31 after MTBI. WM latencies did not differ between male and female mice after MTBI, but ovariectomized mice demonstrated longer latencies over the testing period (P = 0.04; ANOVA).
- Citation: Umeano O, Wang H, Dawson H, Lei B, Umeano A, Kernagis D, James ML. Female gonadal hormone effects on microglial activation and functional outcomes in a mouse model of moderate traumatic brain injury. World J Crit Care Med 2017; 6(2): 107-115
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v6/i2/107.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v6.i2.107