Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Crit Care Med. Feb 4, 2017; 6(1): 37-47
Published online Feb 4, 2017. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v6.i1.37
Published online Feb 4, 2017. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v6.i1.37
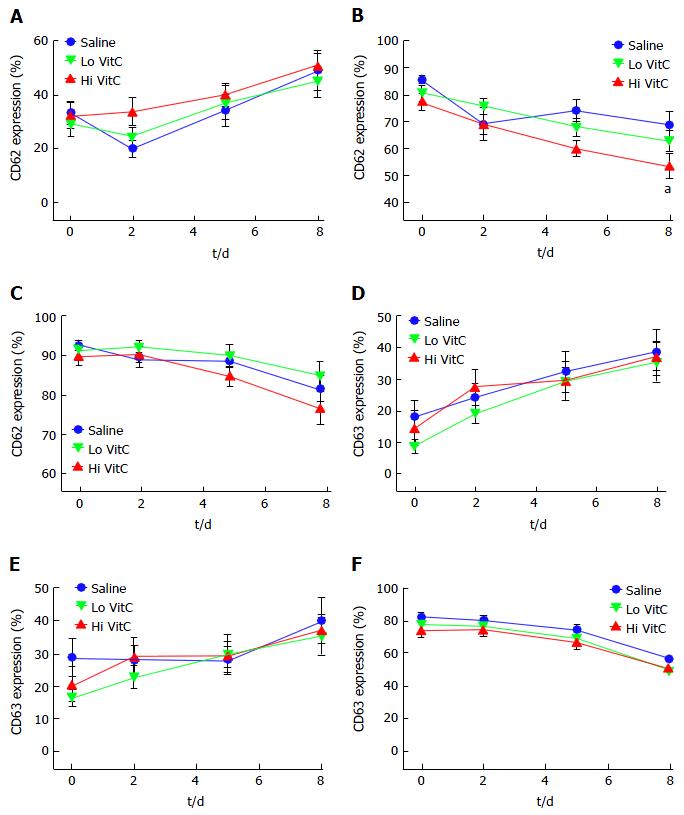
Figure 6 Vitamin C exposure did not significantly alter basal or agonist-stimulated CD62 or CD63 expression profiles.
Flow cytometry showed that basal expression of both CD62 (A) and CD63 (D) did not differ with the addition of Lo/Hi VitC. ADP-stimulated CD62 (B) expression was lower on day 8 in the Hi VitC group (n = 10/group, aP < 0.05), but CD63 (E) expression was not. Thrombin-stimulated CD62 (C) and CD63 (F) expression also did not differ across the three groups (n = 10/group). VitC: Vitamin C; ADP: Adenosine diphosphate.
- Citation: Mohammed BM, Sanford KW, Fisher BJ, Martin EJ, Contaifer Jr D, Warncke UO, Wijesinghe DS, Chalfant CE, Brophy DF, Fowler III AA, Natarajan R. Impact of high dose vitamin C on platelet function. World J Crit Care Med 2017; 6(1): 37-47
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v6/i1/37.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v6.i1.37