Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Crit Care Med. Feb 4, 2017; 6(1): 37-47
Published online Feb 4, 2017. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v6.i1.37
Published online Feb 4, 2017. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v6.i1.37
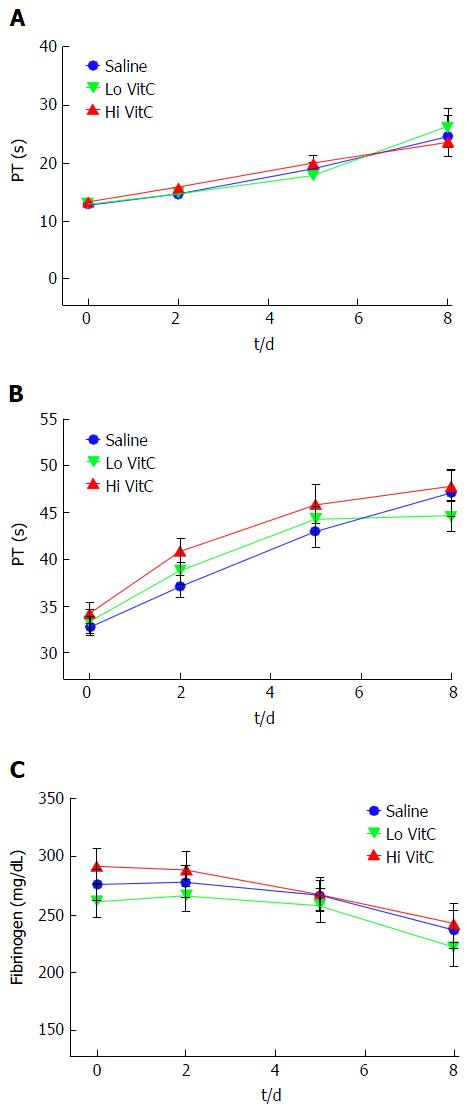
Figure 3 Vitamin C exposure did not alter coagulation pathways in platelets.
PT, PTT and Fibrinogen were performed to detect major impacts on the intrinsic, extrinsic and common coagulation pathways. Using platelet poor plasma we observed no significant changes across the saline, Lo- and Hi VitC groups in the PT (A), PTT (B), and Fibrinogen (C) profiles over storage (n =10/group). VitC: Vitamin C; PT: Prothrombin time; PTT: Partial thrombplastin time.
- Citation: Mohammed BM, Sanford KW, Fisher BJ, Martin EJ, Contaifer Jr D, Warncke UO, Wijesinghe DS, Chalfant CE, Brophy DF, Fowler III AA, Natarajan R. Impact of high dose vitamin C on platelet function. World J Crit Care Med 2017; 6(1): 37-47
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v6/i1/37.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v6.i1.37