Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Crit Care Med. Feb 4, 2017; 6(1): 21-27
Published online Feb 4, 2017. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v6.i1.21
Published online Feb 4, 2017. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v6.i1.21
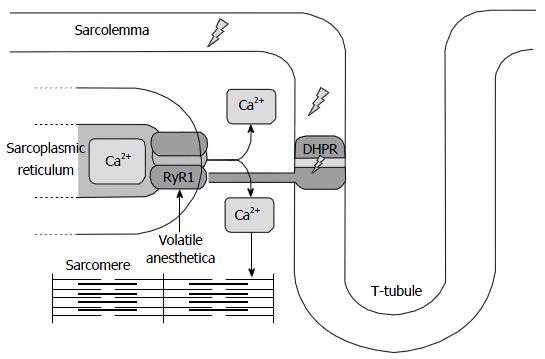
Figure 1 Functional implication of RY1/DHPR receptor mutations after exposure to volatile anesthetics.
The action potential generated in the motor endplate is propagated along the sarcolemma and down the T-tubules, to be captured by the voltage sensitive dihydropyridine receptor. The depolarization-induced conformational change in this receptor in turn results in the opening of the RYR1 calcium-channel and calcium release from the SR. Mutations in the ryanodine-dihydropyridine receptor complex upon exposure to inhalational anesthetics lead to a “longer open state” of RYR1, massive calcium release from the SR, and eventually widespread muscle breakdown.
- Citation: Heytens K, De Bleecker J, Verbrugghe W, Baets J, Heytens L. Exertional rhabdomyolysis and heat stroke: Beware of volatile anesthetic sedation. World J Crit Care Med 2017; 6(1): 21-27
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v6/i1/21.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v6.i1.21