Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Crit Care Med. Feb 4, 2016; 5(1): 47-56
Published online Feb 4, 2016. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v5.i1.47
Published online Feb 4, 2016. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v5.i1.47
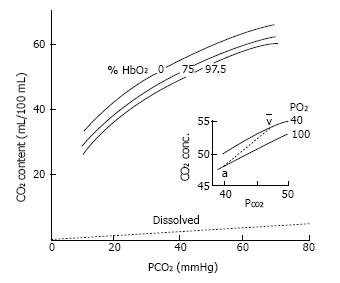
Figure 1 CO2 dissociation curve.
CO2 content (mL/100 mL) vs CO2 partial tension (PCO2). Differences between the curves result in higher CO2 content in the blood, and smaller PCO2 differences between arterial and venous blood. Hemoglobin-O2 saturation affects the position of the CO2 dissociation curve (Haldane effect).
- Citation: Mallat J, Lemyze M, Tronchon L, Vallet B, Thevenin D. Use of venous-to-arterial carbon dioxide tension difference to guide resuscitation therapy in septic shock. World J Crit Care Med 2016; 5(1): 47-56
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v5/i1/47.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v5.i1.47