Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Crit Care Med. Jun 9, 2025; 14(2): 101708
Published online Jun 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i2.101708
Published online Jun 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i2.101708
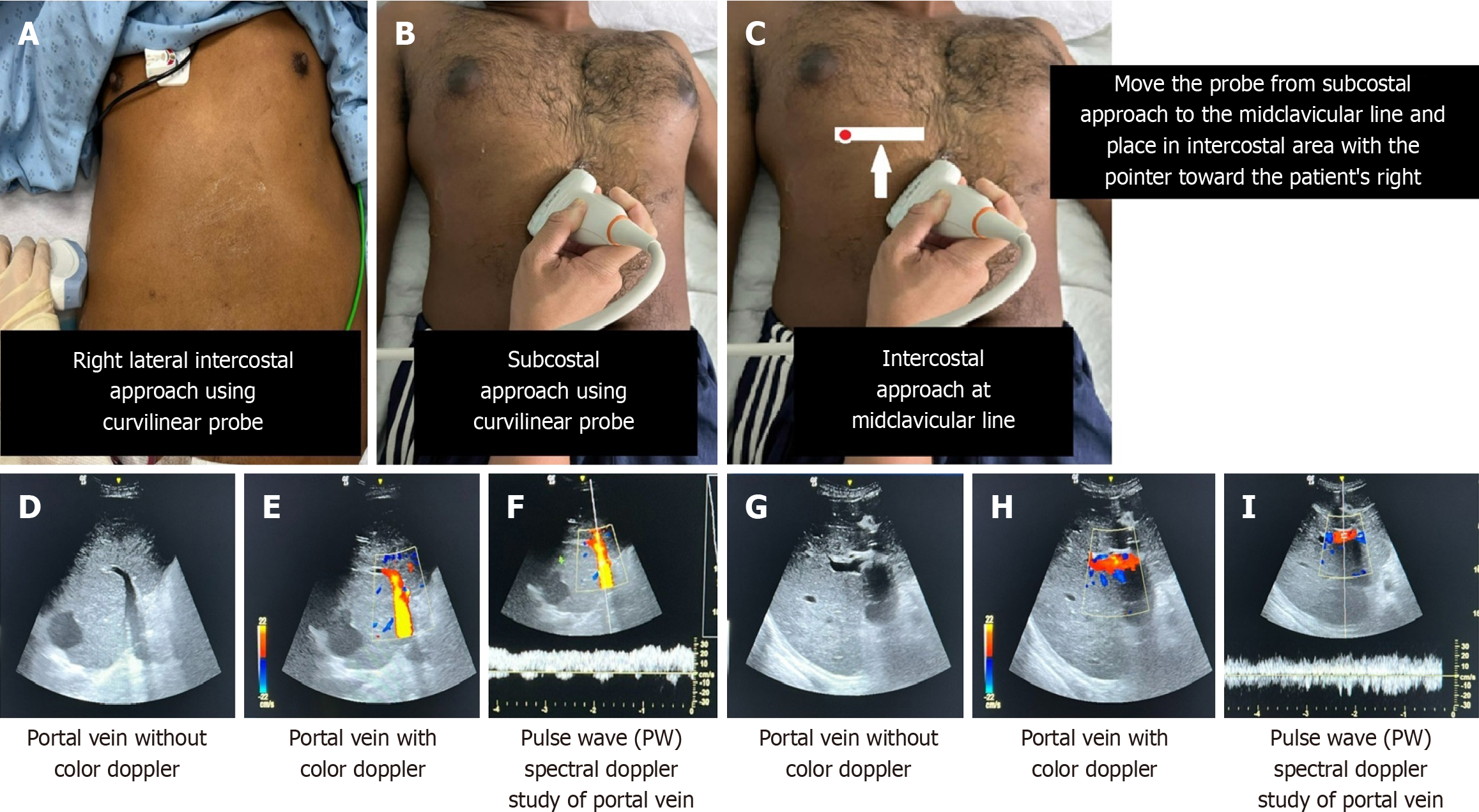
Figure 6 Measures for locating the portal vein using a curvilinear probe and performing a pulse wave spectral Doppler study on the portal vein.
On the left-hand side of the image, we locate the portal vein using the right lateral intercostal or subcostal approach. A: Right lateral intercostal approach; B: Subcostal approach. On the right-hand side of the image, we locate the portal vein using the intercostal approach at the midclavicular line; C: Intercostal approach at the midclavicular line. The portal vein images on each side exhibit slight differences, as do the insonation angles of the portal vein and the pulse wave gate; D-F: Right lateral intercostal or subcostal approach will give an insonation angle of near 0 degree; G-I: Intercostal approaches at the midclavicular line will give an insonation angle of near 90 degrees, which could underestimate the flow velocity measurement.
- Citation: Chin WV, Ngai MMI, See KC. Venous excess ultrasound: A mini-review and practical guide for its application in critically ill patients. World J Crit Care Med 2025; 14(2): 101708
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v14/i2/101708.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v14.i2.101708