Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Crit Care Med. Jun 9, 2025; 14(2): 101708
Published online Jun 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i2.101708
Published online Jun 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i2.101708
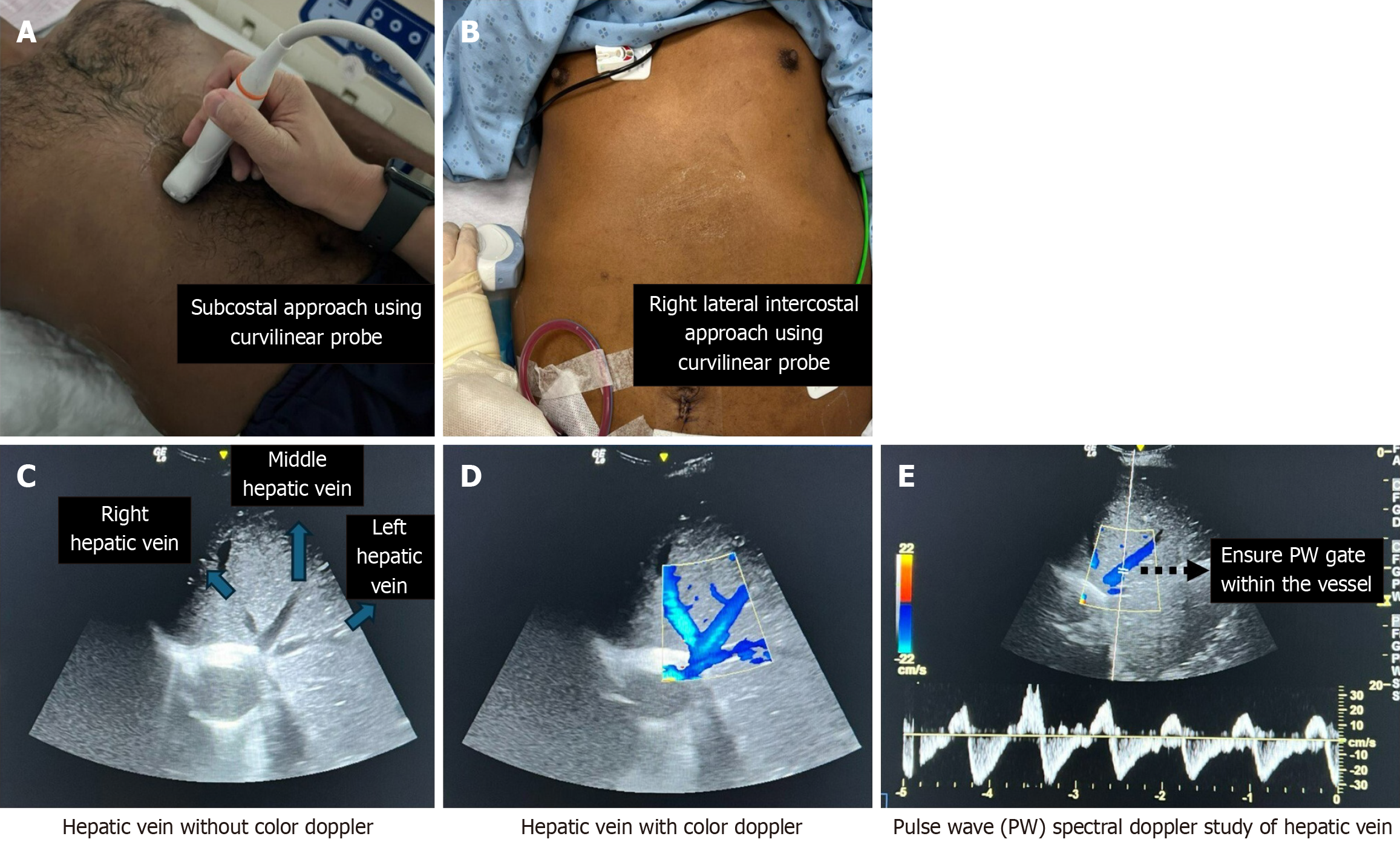
Figure 5 Measures for locating the hepatic vein using a curvilinear probe and performing a pulse wave spectral Doppler study on the hepatic vein.
Locating the hepatic vein using either the subcostal approach or the right lateral intercostal approach, with the pointer directed cephalad and towards the patient's right. A: Subcostal approach; B: Right lateral intercostal approach; C: Hepatic veins consist of right, middle, and left hepatic veins; any one of them can be analyzed for Venous Excess Ultrasound; D: Activating the color Doppler revealed the hepatic vein in blue; E: Once identified, place the pulse wave sample volume, also known as the PW gate, within the hepatic vein.
- Citation: Chin WV, Ngai MMI, See KC. Venous excess ultrasound: A mini-review and practical guide for its application in critically ill patients. World J Crit Care Med 2025; 14(2): 101708
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v14/i2/101708.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v14.i2.101708