Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Crit Care Med. Jun 9, 2024; 13(2): 93812
Published online Jun 9, 2024. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v13.i2.93812
Published online Jun 9, 2024. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v13.i2.93812
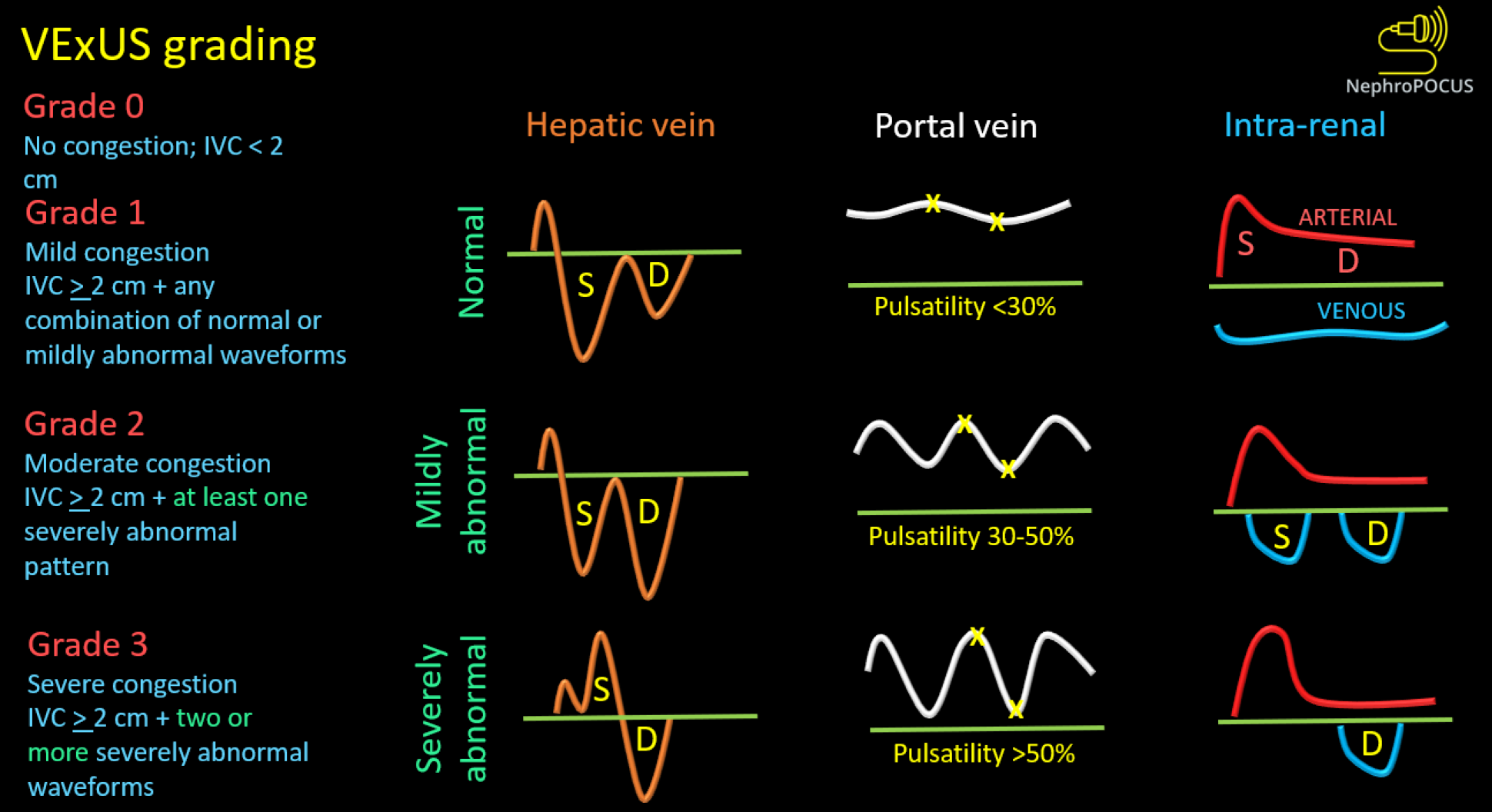
Figure 8 Venous excess ultrasound grading system.
When the diameter of inferior vena cava is ≥ 2 cm, three grades of congestion are defined based on the severity of abnormalities on hepatic, portal, and intrarenal venous Doppler. Hepatic vein Doppler is considered mildly abnormal when the systolic (S) wave is smaller than the diastolic (D) wave, but still below the baseline; it is considered severely abnormal when the S-wave is reversed. Portal vein Doppler is considered mildly abnormal when the pulsatility is 30% to 50%, and severely abnormal when it is ≥ 50%. Asterisks represent points of pulsatility measurement. Renal parenchymal vein Doppler is mildly abnormal when it is pulsatile with distinct S and D components, and severely abnormal when it is monophasic with D-only pattern. Reused from NephroPOCUS.com with permission (https://nephropocus.com/about/).
- Citation: Koratala A. Point-of-care ultrasonography in cirrhosis-related acute kidney injury: How I do it. World J Crit Care Med 2024; 13(2): 93812
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v13/i2/93812.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v13.i2.93812