Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Crit Care Med. Jun 9, 2023; 12(3): 153-164
Published online Jun 9, 2023. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v12.i3.153
Published online Jun 9, 2023. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v12.i3.153
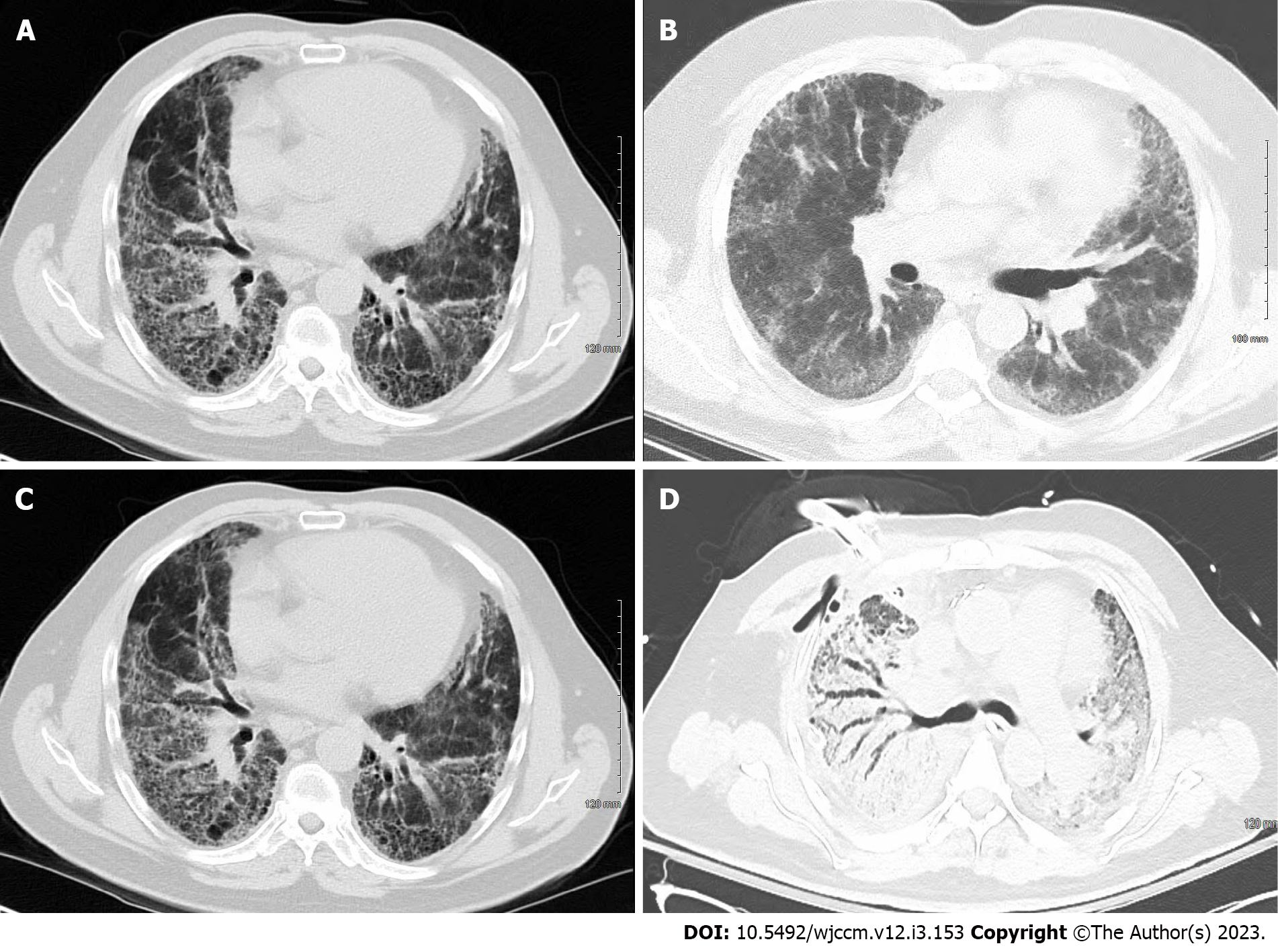
Figure 2 Chest computed tomography.
A: Chest computed tomography (CT) of a patient with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with usual interstitial pneumonia pattern; B: A 54-year-old male with non-specific interstitial pneumonia. Chest CT showed faint ground glass opacity and mild reticulations (non-specific interstitial pneumonia); C: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patient in Figure 2A during acute exacerbation showing ground glass opacities requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation as bridge to transplant; D: Chest CT of patient in Figure 2B during acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease with areas of ground glass opacity and consolidation.
- Citation: Hayat Syed MK, Bruck O, Kumar A, Surani S. Acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease in the intensive care unit: Principles of diagnostic evaluation and management. World J Crit Care Med 2023; 12(3): 153-164
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v12/i3/153.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v12.i3.153