Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Crit Care Med. Jul 9, 2021; 10(4): 102-111
Published online Jul 9, 2021. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v10.i4.102
Published online Jul 9, 2021. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v10.i4.102
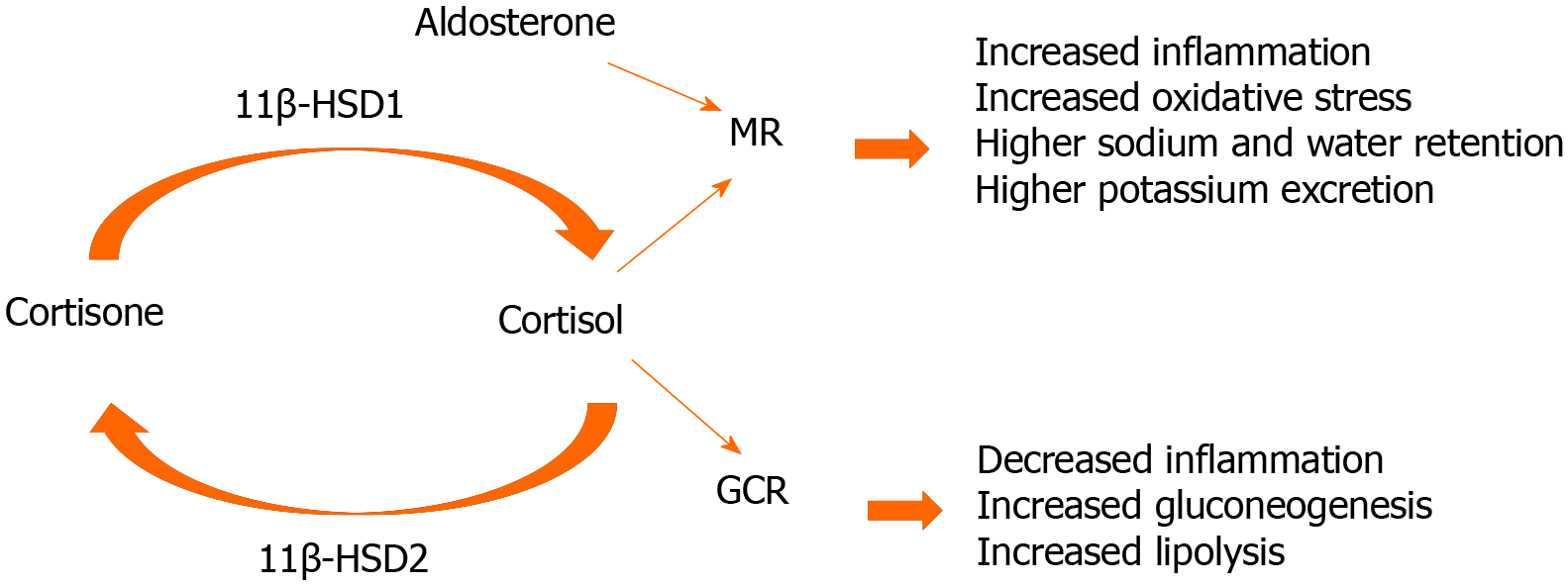
Figure 3 Glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptor function, and the role of 11β-dehydrogenase isozymes.
The ubiquitous glucocorticoid receptor (GCR) binds exclusively to cortisol, whereas the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) is a receptor with equal affinity for mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids. In epithelial tissues, MR activation leads to the expression of proteins regulating ionic and water transports, resulting in the reabsorption of sodium, and as a consequence an increase in extracellular volume, increase in blood pressure, and excretion of potassium to maintain a normal salt concentration in the body. The MR is activated by aldosterone and cortisol. Target cells for aldosterone express the enzyme 11β-dehydrogenase (11β-HSD) 2 that has no effect on aldosterone, but converts cortisol to cortisone, which has only a very weak affinity for the MR In essence, this enzyme “protects” the cell from cortisol and allows aldosterone to act appropriately. 11β-HSD1 activates functionally inert cortisone to active cortisol within target tissues and amplifies local glucocorticoid actions.
- Citation: Vassiliou AG, Athanasiou N, Vassiliadi DA, Jahaj E, Keskinidou C, Kotanidou A, Dimopoulou I. Glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptor expression in critical illness: A narrative review. World J Crit Care Med 2021; 10(4): 102-111
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v10/i4/102.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v10.i4.102