Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
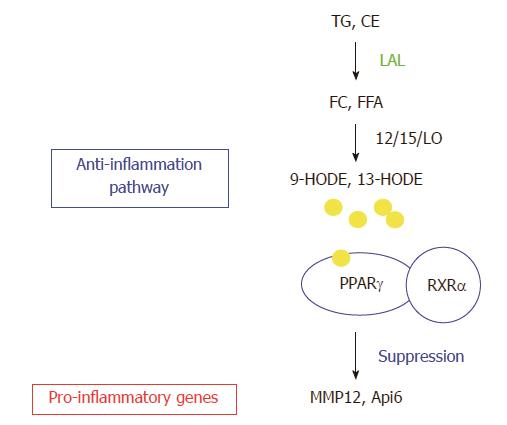
Figure 5 Lysosomal acid lipase and its downstream effector genes.
Lysosomal acid lipase (LAL) cleaves cholesteryl esters (CE) and triglycerides (TG) to produce free cholesterol (FC) and fatty acids (FFA) in lysosomes of cells. The lipid derivatives (9-HODE, 13-HODE) of FFA serve as ligands for PPARγ in coupling with retinoid X receptor α (RXRα, which suppresses gene expression of a variety of pro-inflammatory cytokines. The LAL/PPARγ axis serves as an anti-inflammatory pathway. LAL deficiency blocks this metabolic pathway to provoke up-regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., Api6, MMP12). TGF: Transforming growth factor beta; IL: Interleukin; MCP: Monocyte chemotactic protein; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; NF: Nuclear factor.
- Citation: Yan C, Du H. Lysosomal acid lipase is critical for myeloid-derived suppressive cell differentiation, development, and homeostasis. World J Immunol 2014; 4(2): 42-51
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2824/full/v4/i2/42.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5411/wji.v4.i2.42