Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
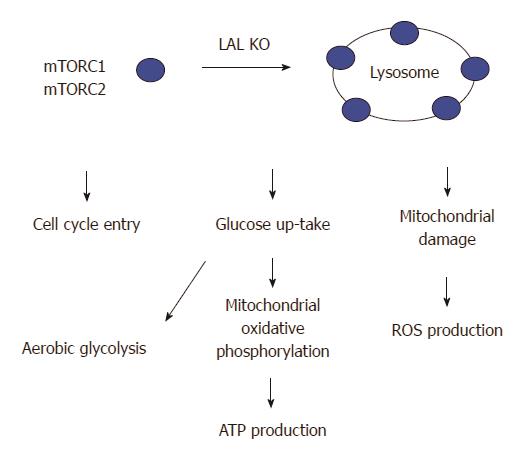
Figure 4 Lysosomal acid lipase deficiency induces overactivation of the mTOR pathway in myeloid-derived suppressive cells.
Lysosomal acid lipase (LAL) is a lysosome-associated enzyme. LAL deficiency increases mTOR complexes anchoring on lysosomes and stimulates the mTOR1 activity to influence the cellular metabolism and proliferation of lal-/- myeloid-derived suppressive cells (MDSCs). These include an increased influx of glucose through aerobic glycolysis, an increased mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production, an impairment of the mitochondrial membrane potential in association with increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and an increased cell cycle entry in lal-/- MDSCs.
- Citation: Yan C, Du H. Lysosomal acid lipase is critical for myeloid-derived suppressive cell differentiation, development, and homeostasis. World J Immunol 2014; 4(2): 42-51
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2824/full/v4/i2/42.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5411/wji.v4.i2.42