Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Clin Urol. Mar 24, 2017; 6(1): 18-26
Published online Mar 24, 2017. doi: 10.5410/wjcu.v6.i1.18
Published online Mar 24, 2017. doi: 10.5410/wjcu.v6.i1.18
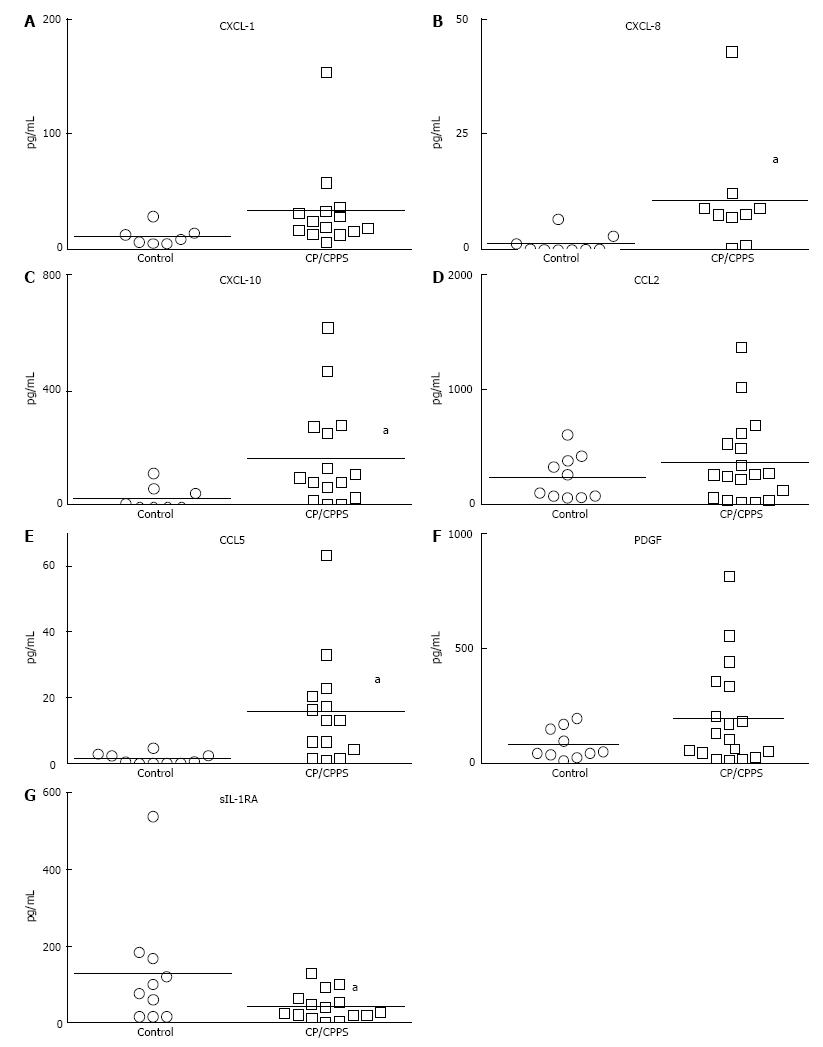
Figure 1 Comparative baseline levels of cytokines, CXC and CC chemokines and growth factors in urine obtained from asymptomatic individuals and chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome patients.
A-C: Urine levels of CXCL-1, CXCL-8 and CXCL-10 chemokines at baseline were significantly elevated in CP/CPPS patients (aP < 0.05). Quantitatively, levels of CXCL-10 (169.8 ± 46.38 pg/mL vs 31.45 ± 16.83 pg/mL) that attract lymphocytes were higher relative to other CXC chemokines CXCL-1 and CXCL-8 that attract neutrophils (notice scale on y-axis). Levels of CC chemokine, CCL-5 (RANTES) also chemotactic for lymphocytes (E) were significantly elevated in CP/CPPS relative to controls (aP < 0.05). Lymphocytic infiltration previously noted in biopsy of CP/CPPS patients is also consistent with significantly lower levels of sIL-1RA in CP/CPPS (G) compared to controls (aP < 0.05). Due to high variability in control group, results were not significant with respect to CCL2 and PDGF (D and F, respectively). Horizontal bars represent mean of the group and Mann-Whitney U test was used for unpaired comparison and chemokines with significant difference appear in bold. CP/CPPS: Chronic prostatitis/ronic pelvic pain syndrome; sIL-1RA: Soluble interleukin-1 receptor antagonist.
- Citation: Tyagi P, Killinger K, McLennan G, Jayabalan N, Chancellor M, Peters KM. Urine chemokine levels correlate with treatment response to phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor in prostatitis. World J Clin Urol 2017; 6(1): 18-26
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2816/full/v6/i1/18.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5410/wjcu.v6.i1.18