Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Pediatr. Mar 9, 2025; 14(1): 99288
Published online Mar 9, 2025. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v14.i1.99288
Published online Mar 9, 2025. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v14.i1.99288
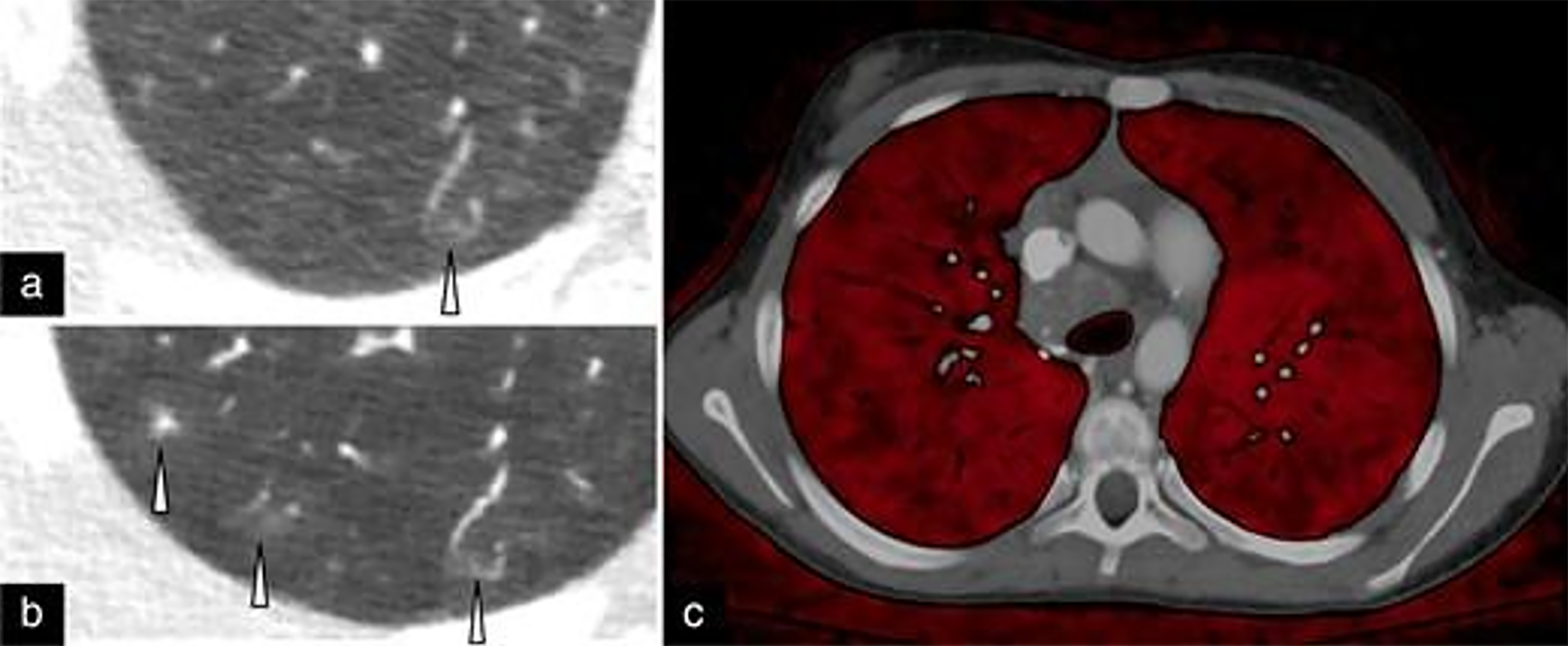
Figure 2 An example of multienergy chest computed tomography with intravenous contrast acquired using the ultra-high-resolution mode with a photon-counting detector computed tomography in a 12-year-old female with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.
a: A previous energy-integrating detector computed tomography (CT) 0.75 mm image displays only one of three small; b: Peripheral arteriovenous malformations (arrowheads) show the photon-counting detector CT 0.8 mm image at the same level; c: In addition to high-resolution images, simultaneous multienergy acquisition on photon-counting detector CT displays the heterogeneous perfusion of the lung parenchyma and permits calculation of lung blood perfusion volume. Copyright ©Siemens Healthineers AG 2024. See: https://www.siemens-healthineers.com/press/copyright#:~:text=Press%20materials%3A%20Copyright&text=Materials%20used%20for%20editorial%20purposes,electronically%20manipulated%20form%2C%20is%20prohibited.
- Citation: Perera Molligoda Arachchige AS, Verma Y. Role of photon-counting computed tomography in pediatric cardiovascular imaging. World J Clin Pediatr 2025; 14(1): 99288
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2808/full/v14/i1/99288.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5409/wjcp.v14.i1.99288