Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Pediatr. Mar 9, 2025; 14(1): 99231
Published online Mar 9, 2025. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v14.i1.99231
Published online Mar 9, 2025. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v14.i1.99231
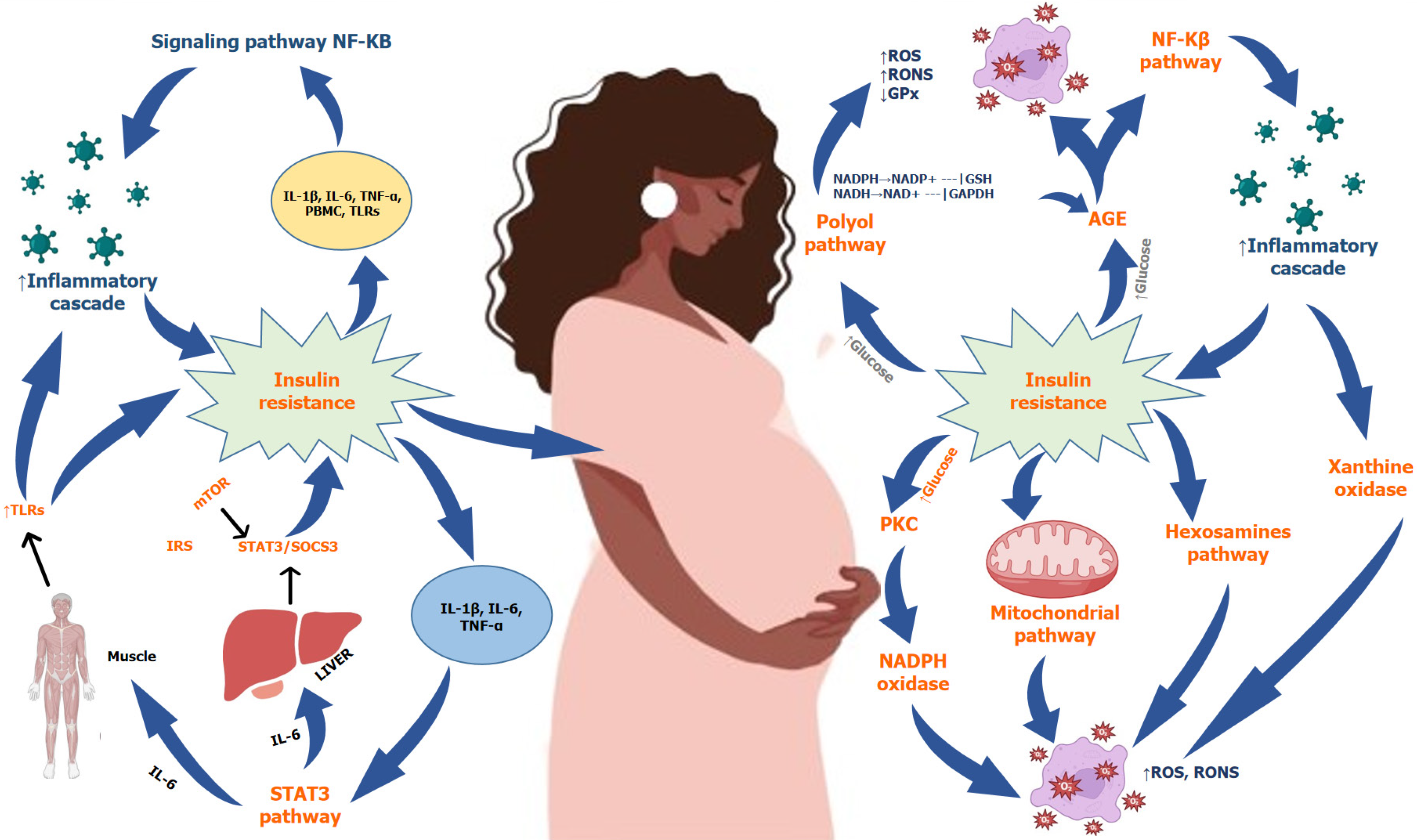
Figure 3 Summarized role of various molecules participate in inflammatory and oxidative stress pathway in the pathophysiology of gestational diabetes mellitus.
IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IRS: Insulin receptor substrates; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; TLRs: Toll-like receptor; RONS: Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; AGE: Advanced glycation end products; PBMC: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells; NADPH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NADH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NADP+: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidized; NAD+: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide oxidized; GPx: Glutathione peroxidase.
- Citation: Shamsad A, Gautam T, Singh R, Banerjee M. Genetic and epigenetic alterations associated with gestational diabetes mellitus and adverse neonatal outcomes. World J Clin Pediatr 2025; 14(1): 99231
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2808/full/v14/i1/99231.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5409/wjcp.v14.i1.99231