Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Respirol. Nov 28, 2013; 3(3): 44-47
Published online Nov 28, 2013. doi: 10.5320/wjr.v3.i3.44
Published online Nov 28, 2013. doi: 10.5320/wjr.v3.i3.44
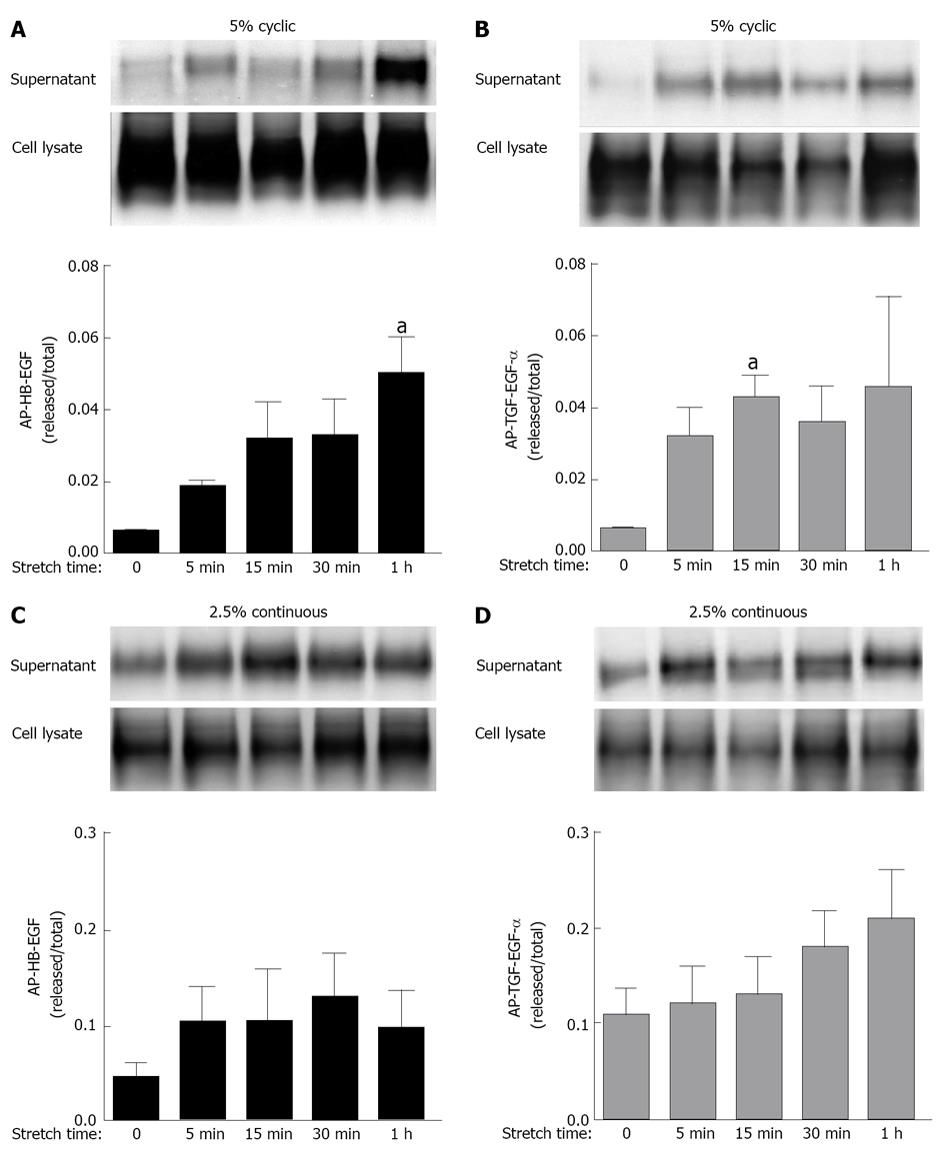
Figure 2 Cyclic mechanical strain releases heparin binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor and transforming growth factor alpha ligands.
Fetal type II cells were transfected by electroporation with cDNA constructs encoding alkaline phosphatase-tagged heparin binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor (HB-EGF) and transforming growth factor alpha (TGF-α) ligands. 24 h later, cells were exposed to 5% cyclic strain or 2.5% continuous strain for the indicated periods of time. Samples were processed to assess ligand-release into the supernatant using the alkaline phosphatase shedding assay protocol. Data are expressed as the intensity of each alkaline phosphatase (AP) supernatant band divided by total AP (supernatant + cell lysate). Upper panels shown representative blots. Data in the lower panels are from three independent experiments. aP < 0.05 vs unstretched samples for 1 h.
- Citation: Sanchez-Esteban J. Growth factors and fetal lung development mediated by mechanical forces. World J Respirol 2013; 3(3): 44-47
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6255/full/v3/i3/44.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5320/wjr.v3.i3.44