Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Respirol. Jul 28, 2013; 3(2): 11-19
Published online Jul 28, 2013. doi: 10.5320/wjr.v3.i2.11
Published online Jul 28, 2013. doi: 10.5320/wjr.v3.i2.11
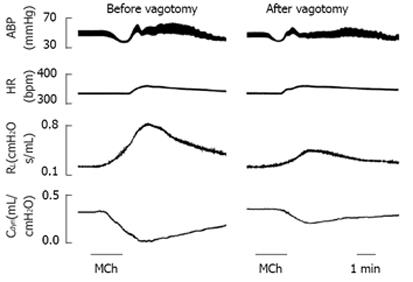
Figure 7 Comparison of the cardiovascular and airway responses to methacholine aerosol (100 μg/mL per minute for 2 min) before and after bivagotomy in an anesthetized and paralyzed Ova-treated guinea pig.
The traces are arterial blood pressure (ABP), heart rate (HR), total lung resistance (RL), and dynamic pulmonary compliance (Cdyn).
- Citation: Zhuang J, Bailet D, Curtis R, Xu F. High-frequency electrical stimulation of cervical vagi reduces airway response to methacholine. World J Respirol 2013; 3(2): 11-19
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6255/full/v3/i2/11.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5320/wjr.v3.i2.11