Copyright
©2013 Baishideng.
World J Otorhinolaryngol. Feb 28, 2013; 3(1): 1-15
Published online Feb 28, 2013. doi: 10.5319/wjo.v3.i1.1
Published online Feb 28, 2013. doi: 10.5319/wjo.v3.i1.1
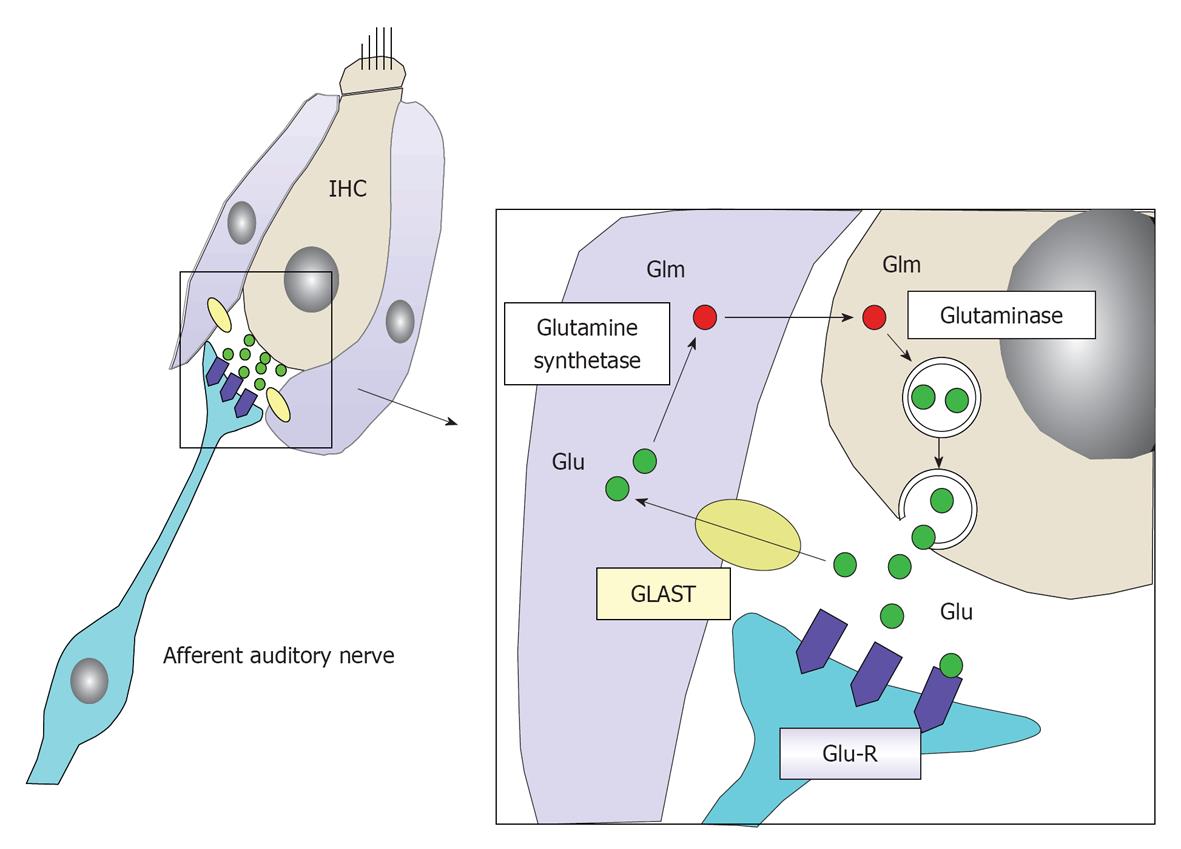
Figure 24 Schematic drawing of glutamate recycle system as a neurotransmitter between inner hair cells and the primary auditory neuron.
Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter between inner hair cells (IHCs) and primary auditory neurons. It is released into the synaptic cleft in response to depolarization of IHCs. After stimulating a primary auditory neuron by binding to a glutamate receptor (Glu-R), it is absorbed by the surrounding supporting cells (inner phalangeal cell and inner pillar cells) by means of glutamate-aspartate transporter (GLAST). It is transformed into glutamine, and then transported to IHCs and stored in a vesicle until the next depolarization of the IHC. In this way, the glutamate is recycled.
- Citation: Gyo K. Experimental study of transient cochlear ischemia as a cause of sudden deafness. World J Otorhinolaryngol 2013; 3(1): 1-15
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6247/full/v3/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5319/wjo.v3.i1.1