Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Ophthalmol. Nov 12, 2014; 4(4): 92-112
Published online Nov 12, 2014. doi: 10.5318/wjo.v4.i4.92
Published online Nov 12, 2014. doi: 10.5318/wjo.v4.i4.92
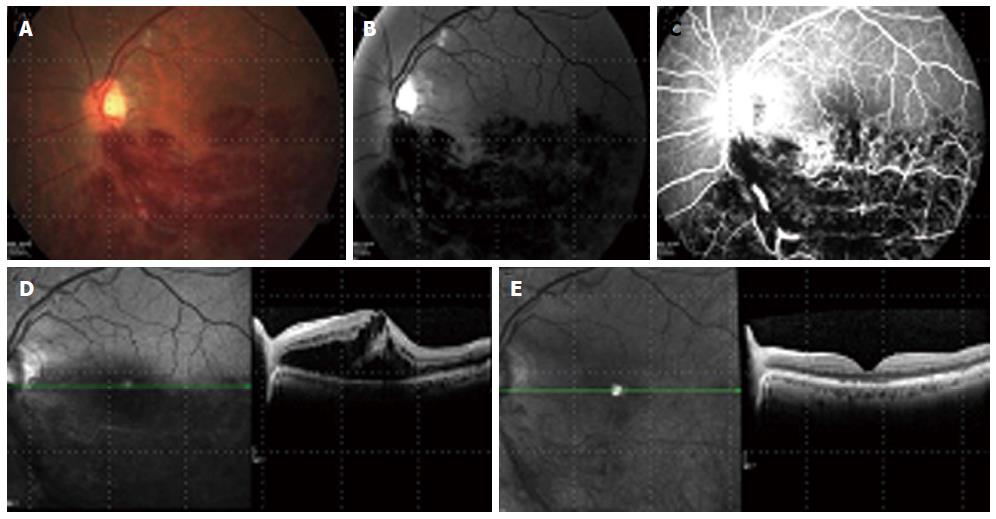
Figure 1 Left eye branch retinal vein occlusion with cystoid macular edema presented in color picture, red free and fluorescein angiography (A-C).
A before treatment spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) of the macula (D) showing loss of foveal contour with increased central macular thickness due to many intra-retinal large cystoids spaces and sub-retinal fluid accumulation. (E) SD-OCT 2 mo later, after 2 intravitreal bevacizumab injections, 1 mo apart. A normal foveal contour with some sub-foveal outer segment abnormalities. A decrease in retinal thickness back to normal and complete resolution of cystoid macular edema and sub-retinal fluid.
- Citation: Keren S, Loewenstein A, Coscas G. Pathogenesis, prevention, diagnosis and management of retinal vein occlusion. World J Ophthalmol 2014; 4(4): 92-112
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6239/full/v4/i4/92.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5318/wjo.v4.i4.92