Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Obstet Gynecol. Feb 10, 2016; 5(1): 39-49
Published online Feb 10, 2016. doi: 10.5317/wjog.v5.i1.39
Published online Feb 10, 2016. doi: 10.5317/wjog.v5.i1.39
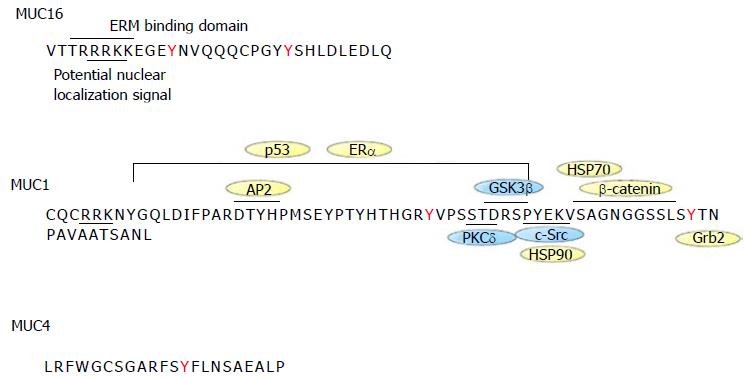
Figure 2 Sequence of MUC1, MUC4 and MUC16 cytoplasmic tails.
The intracellular sequence of the different mucins is shown along with protein interaction sites. MUC1 is the best characterized mucin. MUC1 cytoplasmic tail interacts with c-Src, GSK3β, PCKδ, β-catenin, p53, ERα, HSP70/90, Grb2, AP-2. Proteins with kinase activity are in blue whereas those without kinase activity are in yellow. HSP70 binds to MUC1 cytoplasmic tail in the same region as β-catenin. HSP90 binding to MUC1 depends on c-Src-induced Y-46 phosphorylation. MUC16 cytoplasmic tail has an ERM motif for potential interaction with the cytoskeleton. Both MUC1 and MUC16 contain a potential nuclear localization signal motif. MUC4 has no known interaction binding partners. EMR: Ezrin/radixin/moesin.
- Citation: Piché A. Pathobiological role of MUC16 mucin (CA125) in ovarian cancer: Much more than a tumor biomarker. World J Obstet Gynecol 2016; 5(1): 39-49
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6220/full/v5/i1/39.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5317/wjog.v5.i1.39