Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
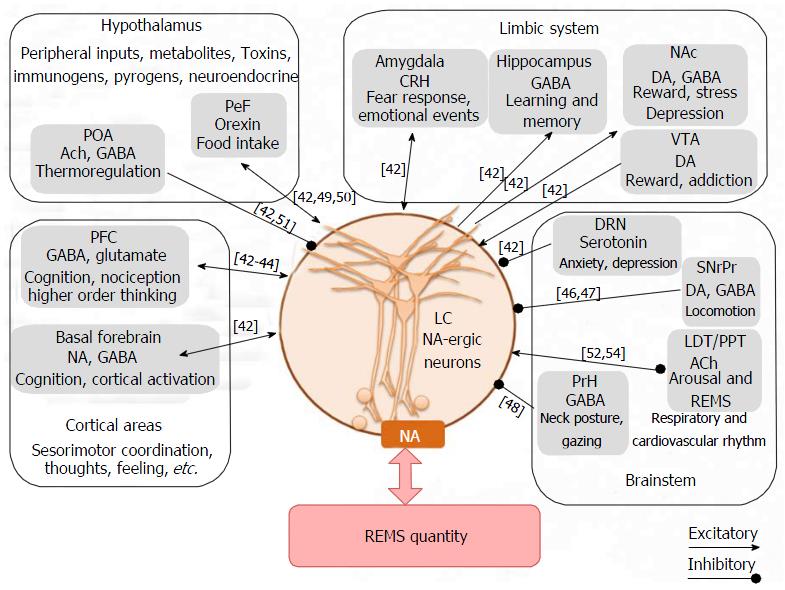
Figure 1 Schematic illustration of inputs to the locus coeruleus neurons from different regions in the brain, some of them are influenced by the environmental changes.
The resultant output of the LC neurons is responsible for level of NA in the brain. As those LC-NA-ergic neurons cease activity during REMS, disturbance in the latter keeps those neurons active and thus modulates NA level in the brain. This altered level of NA (mostly elevated level) in turn affects physiological processes regulated by the brain. PFC: Prefrontal cortex; NAc: Nucleus accumbens; VTA: Ventral tagmental area; DRN: Dorsal raphe nucleus; SNrPr: Substantia niagra pars reticulate; PrH: Prepositus hypoglossus; PeF: Perifornical area; POA: Preoptic area; LDT/PPT: Laterodorsal tegmentumpedunculopontine tegmentum; LC: Locus coeruleus; ACh: Acetylcholine; DA: Dopamine; GABA: Gamma-amino butyric acid; NA: Noradrenaline.
- Citation: Mehta R, Singh A, Mallick BN. Disciplined sleep for healthy living: Role of noradrenaline. World J Neurol 2017; 7(1): 6-23
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6212/full/v7/i1/6.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5316/wjn.v7.i1.6