Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
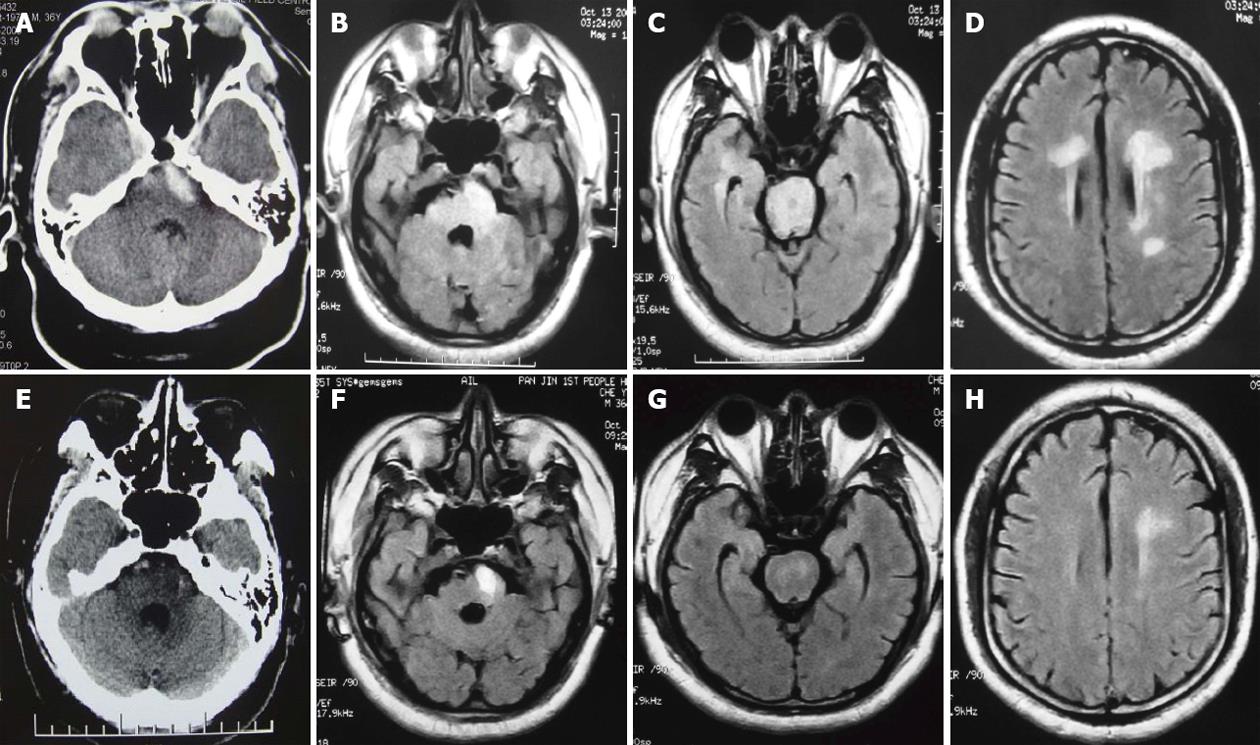
Figure 1 The imagings before admission and after 17 d.
A: Initial computed tomography (CT) shows the left basilar part of pons hemorrhage; B, C: Initial fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery (FLAIR) show hyperintense signals in the pons and bilateral periventricular, anterior part of bilateral centrum ovale; D: Follow-up CT 17 d after initial imaging, showing low-density signal changes in the left basilar part of pons, indicating pontine hemorrhage has been almost absorbed (E); F, G: Follow-up FLAIR 17 d after initial imaging, showing a nearly complete resolution of hyperintensity except hemorrhage in the pons and bilateral periventricular, anterior part of bilateral centrum ovale (H).
- Citation: Zhou ZH, Qu F, Chen HS. Hypertensive brain stem encephalopathy with pontine hemorrhage: A case report. World J Neurol 2013; 3(3): 83-86
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6212/full/v3/i3/83.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5316/wjn.v3.i3.83