Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
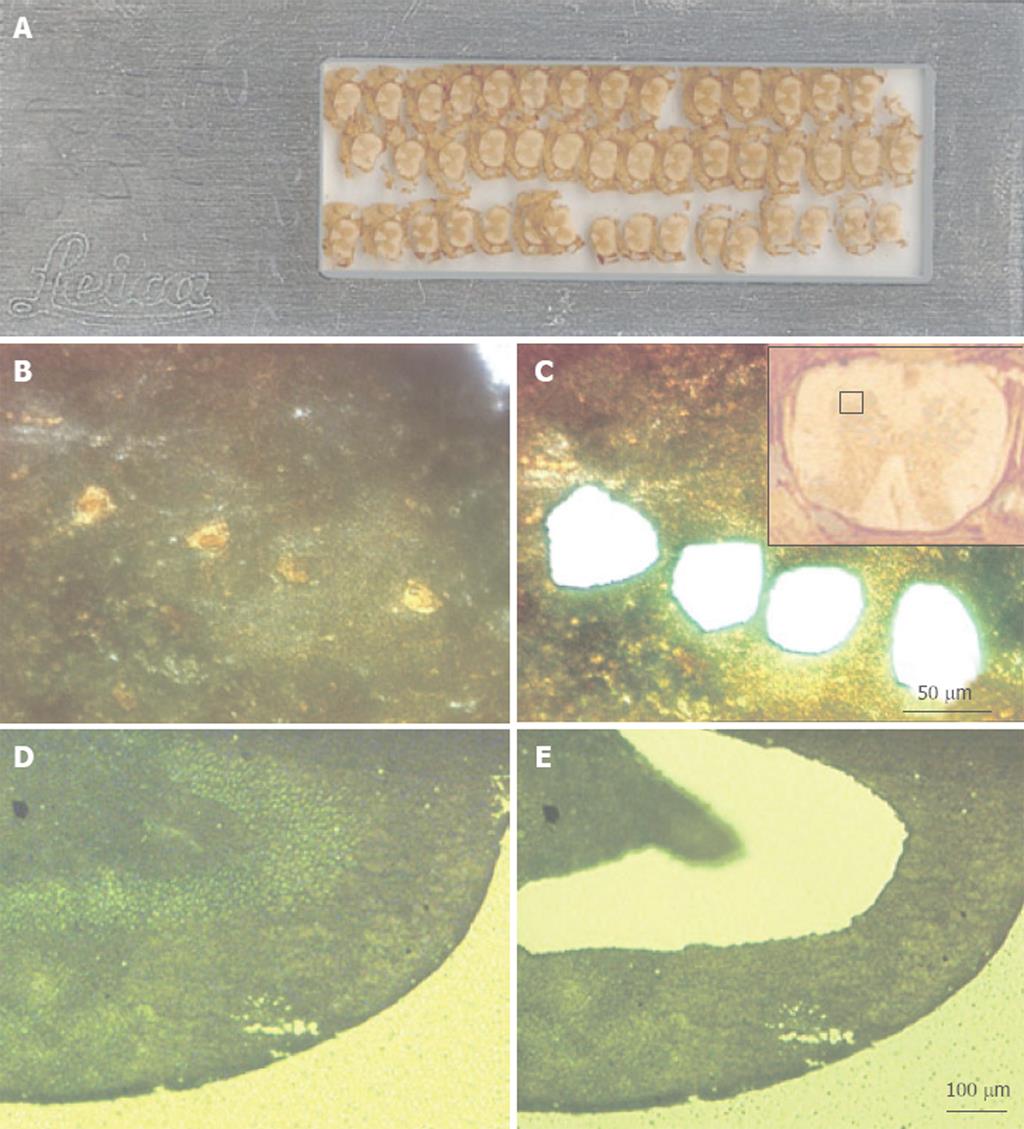
Figure 1 Examples of tissues following microdissection using a Leica DMLA laser-assisted microdissection system.
A: A scanned image of a foil slide with multiple coronal sections of mouse spinal cord mounted. These sections are 16 μm thick; B: A high-power (× 40 objective, × 400 final magnification) image of the ventral gray region of mouse spinal cord that was immuno-stained for the NeuN neuronal marker. The yellow-brown profiles are motor neurons; C: The same view as in panel B, but after laser microdissection and collection of four motor neurons; C: A low-power (× 5 objective, × 50 final magnification) image of the spinal cord section (shown upside down), with the red square marking the region shown in panels B and C; D: A low-power view (× 10 objective, × 100 final magnification) of methyl green-stained rat dentate gyrus. The section is 10 μm thick; E: An image of the same section shown in panel D, but after microdissection and collection of the neurons in the granule cell layer.
- Citation: He Z, Cui L, He B, Ferguson SA, Paule MG. A common genetic mechanism underlying susceptibility to posttraumatic stress disorder. World J Neurol 2013; 3(3): 14-24
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6212/full/v3/i3/14.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5316/wjn.v3.i3.14