Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
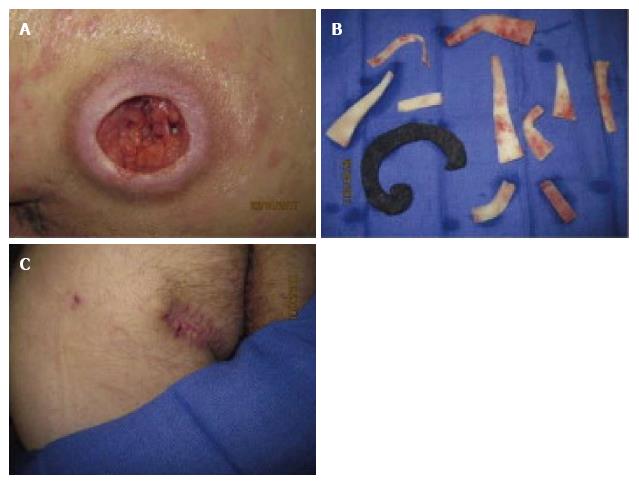
Figure 8 Infection and sepsis, foam retention in the wound, tissue adherence, bleeding, and pain[2].
A: Treatment of L-1 partial paralysis and left ischial pressure ulcer with microdeformational wound therapy for 2 m; B: Discovery of retained foam; C: Wound healing following removal of foreign material and flap surgery. Courtesy of Brigham and Women's Hospital.
- Citation: Panayi AC, Leavitt T, Orgill DP. Evidence based review of negative pressure wound therapy. World J Dermatol 2017; 6(1): 1-16
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6190/full/v6/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5314/wjd.v6.i1.1