Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
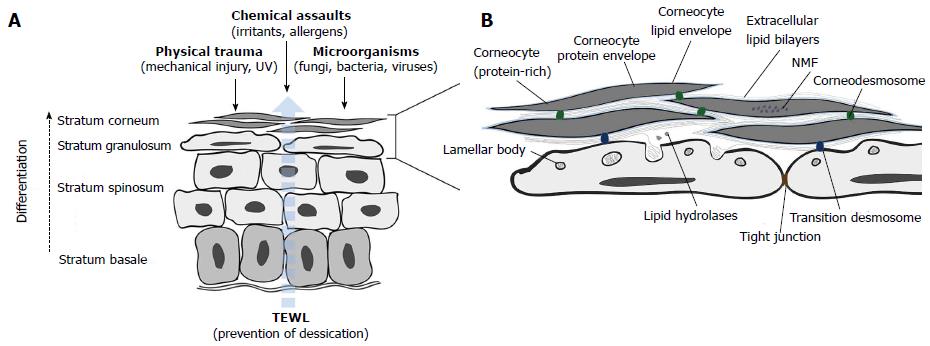
Figure 2 Outside-inside and inside-outside barrier functions of the epidermis.
A: The epidermis forms a barrier against multiple external threats and prevents excessive transepidermal water loss (TEWL, indicated by the dashed blue arrow) from the interior of the body; B: Components of the stratum corneum (SC) and stratum granulosum (SG) barriers. During terminal differentiation of SG keratinocytes into corneocytes, lamellar bodies (LBs) fuse with the plasma membrane and their contents is extruded at the SG-SC interface. LB-derived lipids are processed and arranged into continuous bilayers parallel to the corneocyte surface using the covalently bound corneocyte lipid envelope (pale blue) as a scaffold. NMF: Natural moisturising factor.
- Citation: Gillespie RM, Brown SJ. From the outside-in: Epidermal targeting as a paradigm for atopic disease therapy. World J Dermatol 2015; 4(1): 16-32
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6190/full/v4/i1/16.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5314/wjd.v4.i1.16