Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Orthop. Oct 18, 2016; 7(10): 638-649
Published online Oct 18, 2016. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v7.i10.638
Published online Oct 18, 2016. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v7.i10.638
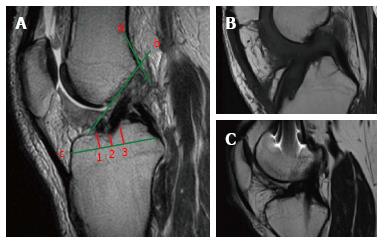
Figure 4 On the sagittal plane, the front border of the tibial tunnel.
It should be localized behind a line that is tangential to the Blumensaat line (line b); however, without going beyond the midpoint of the proximal tibia with the knee in full extension. The femoral tunnel should be located at the intersection of the posterior femoral cortex (line a) and the lateral wall of the intercondylar notch (line b). The position of the tibial tunnel entrance is measured as following: the total antero-posterior diameter of the tibial plateau (line c) is measured in the sagittal slice where the tibial entrance is better visualized. The location of the anterior margin of the tunnel is obtained dividing the distance from the anterior tibial plateau margin and the most anterior part of the tunnel entrance (point 1) for the total AP diameter (line c) and multiplying for 100. The location of the posterior margin (point 3) and the center of the tunnel (point 2) are obtained similarly (A). Sagittal view with a tibial tunnel positioned anterior to the midpoint of the tibial plateau diameter, resulting in an increased risk of impingement (B). Sagittal view with a tibial tunnel positioned too posterior, resulting in a vertical graft (C). The native ACL is located between the 31% and 63% of the tibial plateau diameter, with its center at 48%. ACL: Anterior cruciate ligament.
- Citation: Grassi A, Bailey JR, Signorelli C, Carbone G, Wakam AT, Lucidi GA, Zaffagnini S. Magnetic resonance imaging after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: A practical guide. World J Orthop 2016; 7(10): 638-649
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v7/i10/638.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v7.i10.638