Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Orthop. Jul 18, 2015; 6(6): 498-504
Published online Jul 18, 2015. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v6.i6.498
Published online Jul 18, 2015. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v6.i6.498
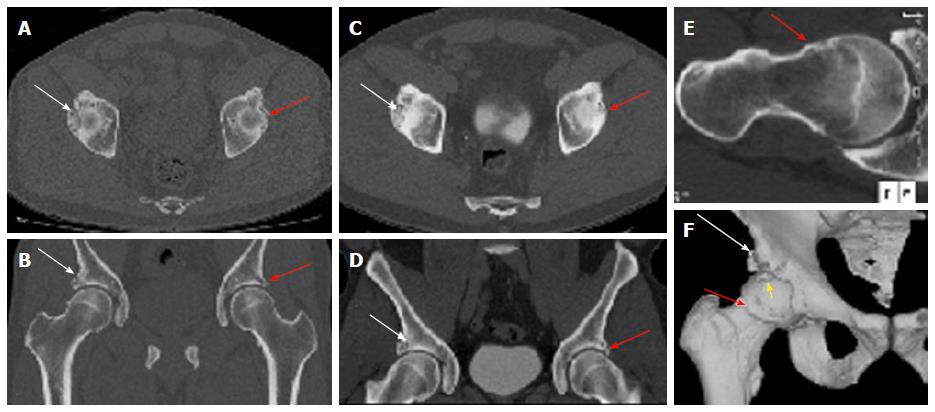
Figure 2 3D computed tomography imaging of the pelvis.
Computed tomography pelvis obtained at current presentation (A, B) and 2 years before (C, D) confirm the unchanged bilateral mixed femoroacetabular impingement anatomy with a chronic right acetabular rim fracture (white arrows) and small left Os acetabulum/labral calcification (yellow arrow). Oblique axial thick slab maximum intensity projection reconstruction (E) along the right femoral neck axis shows the CAM deformity (red arrow) and fibrocystic change at the head and neck junction. Surface rendered 3D bone reconstruction (F) confirms the rim fracture (white arrows) and the CAM deformity (red arrow). Also note loose fragment anteriorly and superiorly, which was subsequently removed on surgery (yellow arrow).
- Citation: Chhabra A, Nordeck S, Wadhwa V, Madhavapeddi S, Robertson WJ. Femoroacetabular impingement with chronic acetabular rim fracture - 3D computed tomography, 3D magnetic resonance imaging and arthroscopic correlation. World J Orthop 2015; 6(6): 498-504
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v6/i6/498.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v6.i6.498