Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Orthop. May 18, 2015; 6(4): 394-399
Published online May 18, 2015. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v6.i4.394
Published online May 18, 2015. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v6.i4.394
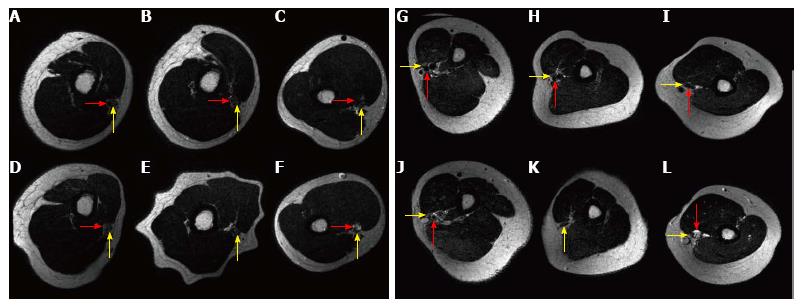
Figure 2 Red arrow indicates brachial artery, yellow arrow indicates median nerve.
A-F: MRI imaging; A-C: Baseline imaging proximal, sulcus and distal humeral arm; D-F: Compression with the broad tourniquet proximal, sulcus and distal humeral arm; G-L: MRI imaging; G-I: Baseline imaging proximal, sulcus and distal humeral arm; J-L: Compression with the narrow tourniquet proximal, sulcus and distal humeral arm. MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
-
Citation: Kovar FM, Jaindl M, Oberleitner G, Endler G, Breitenseher J, Prayer D, Kasprian G, Kutscha-Lissberg F. Nerve compression and pain in human volunteers with narrow
vs wide tourniquets. World J Orthop 2015; 6(4): 394-399 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v6/i4/394.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v6.i4.394