Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Orthop. Apr 18, 2014; 5(2): 134-145
Published online Apr 18, 2014. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v5.i2.134
Published online Apr 18, 2014. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v5.i2.134
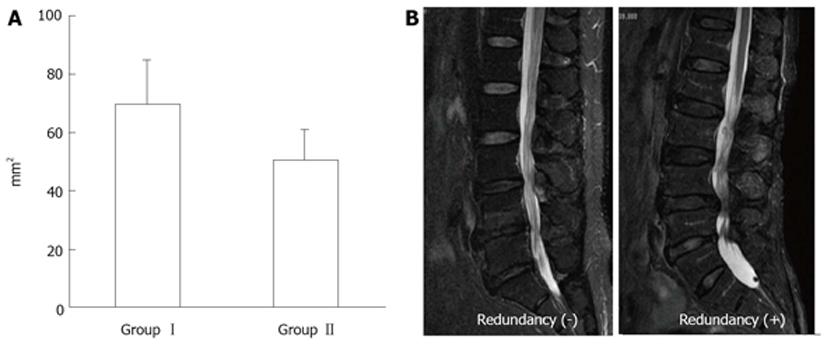
Figure 12 Magnetic resonance imaging of lumbar canal stenosis patients with neurogenic intermittent claudication.
A: Cross-sectional area of dural sac (T1-w) at the site of maximal canal stenosis; B: Magnetic resonance imaging of redundunt nerve root (T2-w).
- Citation: Kobayashi S. Pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of intermittent claudication in patients with lumbar canal stenosis. World J Orthop 2014; 5(2): 134-145
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v5/i2/134.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v5.i2.134