Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Orthop. Oct 18, 2013; 4(4): 267-278
Published online Oct 18, 2013. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v4.i4.267
Published online Oct 18, 2013. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v4.i4.267
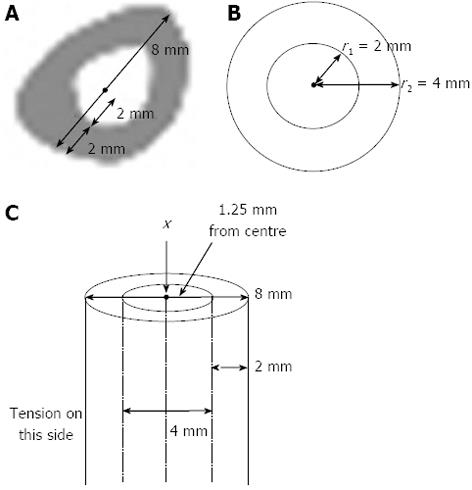
Figure 5 For tension to be produced in a typical beam a similar size to the rabbit tibia, a compressive load needs to be offset from the centroid in the opposite direction by only 1.
25 mm. A: Dimensions from the midshaft of a rabbit’s tibial cross-section: AP width (8 mm), cortical width (2 mm) and medullary half-width (2 mm); B: The rabbit midshaft cross-section represented as a section from a beam; C: The beam showing an axial load through the centroid (x) and the offset.
- Citation: Franklyn M, Field B. Experimental and finite element analysis of tibial stress fractures using a rabbit model. World J Orthop 2013; 4(4): 267-278
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v4/i4/267.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v4.i4.267