Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Orthop. Apr 18, 2025; 16(4): 103388
Published online Apr 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i4.103388
Published online Apr 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i4.103388
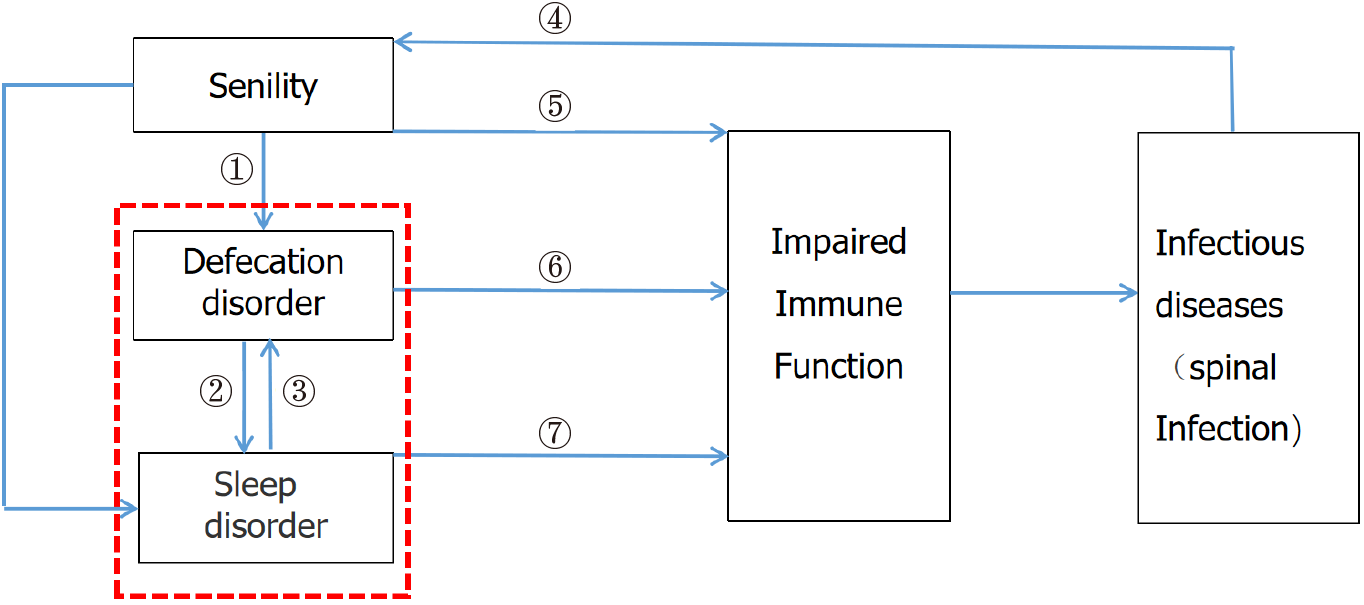
Figure 1 Diagram of potential causes of spinal.
(1) Many older people's nutritional changes lead to changes in intestinal flora and immune capacity; (2) Defecation disorders affect sleep by regulating bacterial metabolites, endocrine signals, nerve signal immunity, etc.; (3) Changes in sleep rhythm lead to changes in intestinal flora composition; (4) Infectious diseases induce aging through a sustained inflammatory immune response; (5) Aging affects the body's immune function through immune aging and inflammatory aging; (6) Defecation disorder affects the immune function of the body by affecting the intestinal shielding barrier, increasing the permeability of the intestinal wall, causing inflammation and immunity; and (7) Sleep disorders affect the immune function of the body by up-regulating adaptive immunity and down-regulating innate immunity. Among them, sleep disorders and defecation disorders show a bidirectional relationship through the brain-gut-microbial axis.
- Citation: Guo LL, Liu HK, Cao JF, Zhang HX, Li B, Li T, Li L. Senility, defecation disorders, sleep disorders, and non-operative spinal infections: A single-center retrospective analysis. World J Orthop 2025; 16(4): 103388
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v16/i4/103388.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v16.i4.103388