Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Orthop. Jan 18, 2025; 16(1): 98871
Published online Jan 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i1.98871
Published online Jan 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i1.98871
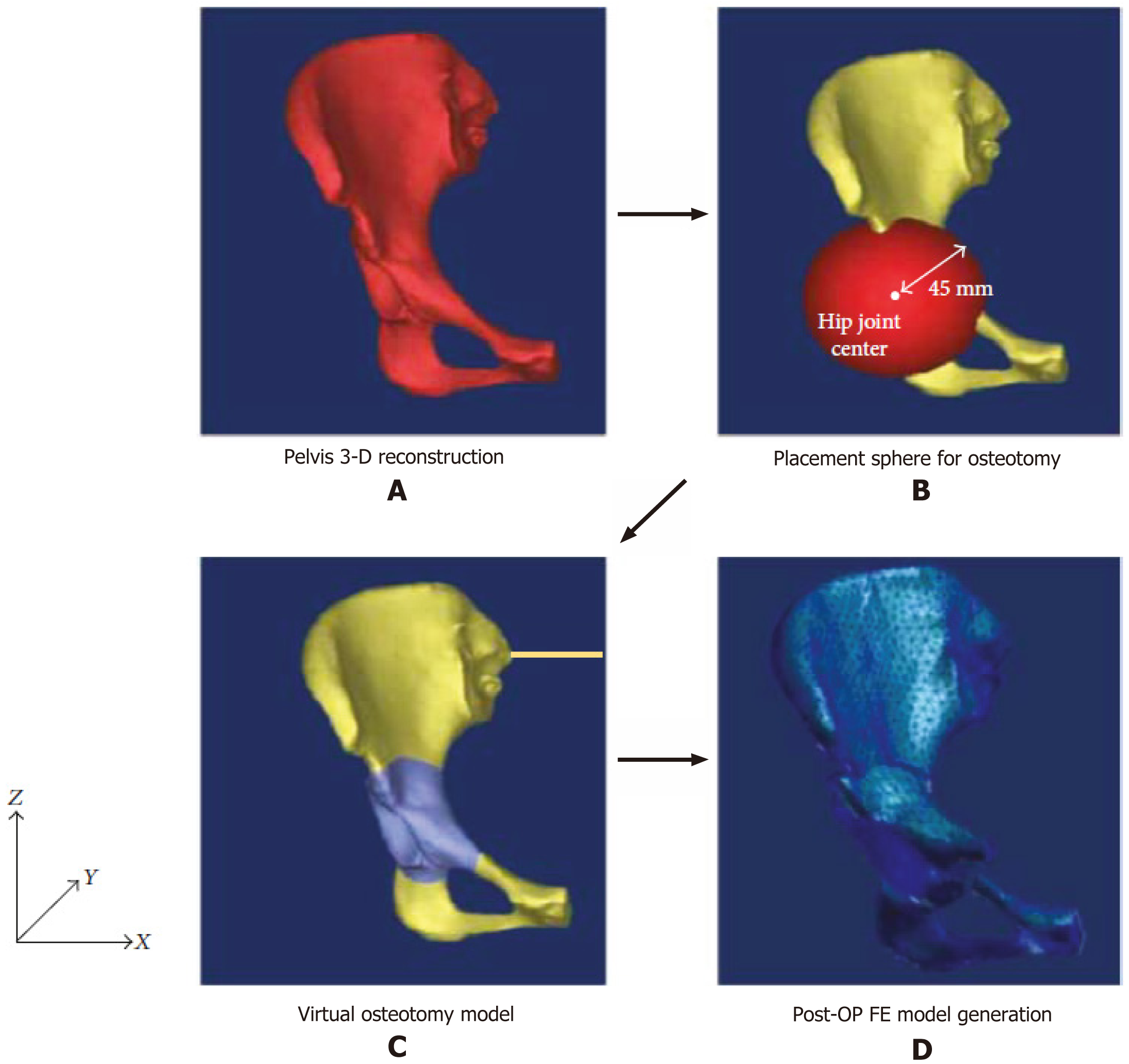
Figure 4 Finite element model using patient’s anatomy-specific[29].
Citation: Park SJ, Lee SJ, Chen WM, Park JH, Cho YS, Shin T, Kwon SY. Computer-Assisted Optimization of the Acetabular Rotation in Periacetabular Osteotomy Using Patient’s Anatomy-Specific Finite Element Analysis. Appl Bionics Biomech 2018; 2018: 9730525. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2018. Published by Hindawi Publishing Corporation. A: Pelvis 3-D reconstruction; B: Placement sphere for osteotomy; C: Virtual osteotomy model; D: Postoperative finite element model generation. Post-OP FE: Postoperative finite element.
- Citation: Ammarullah MI. Integrating finite element analysis in total hip arthroplasty for childhood hip disorders: Enhancing precision and outcomes. World J Orthop 2025; 16(1): 98871
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v16/i1/98871.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v16.i1.98871