Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Orthop. Nov 18, 2024; 15(11): 1056-1074
Published online Nov 18, 2024. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v15.i11.1056
Published online Nov 18, 2024. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v15.i11.1056
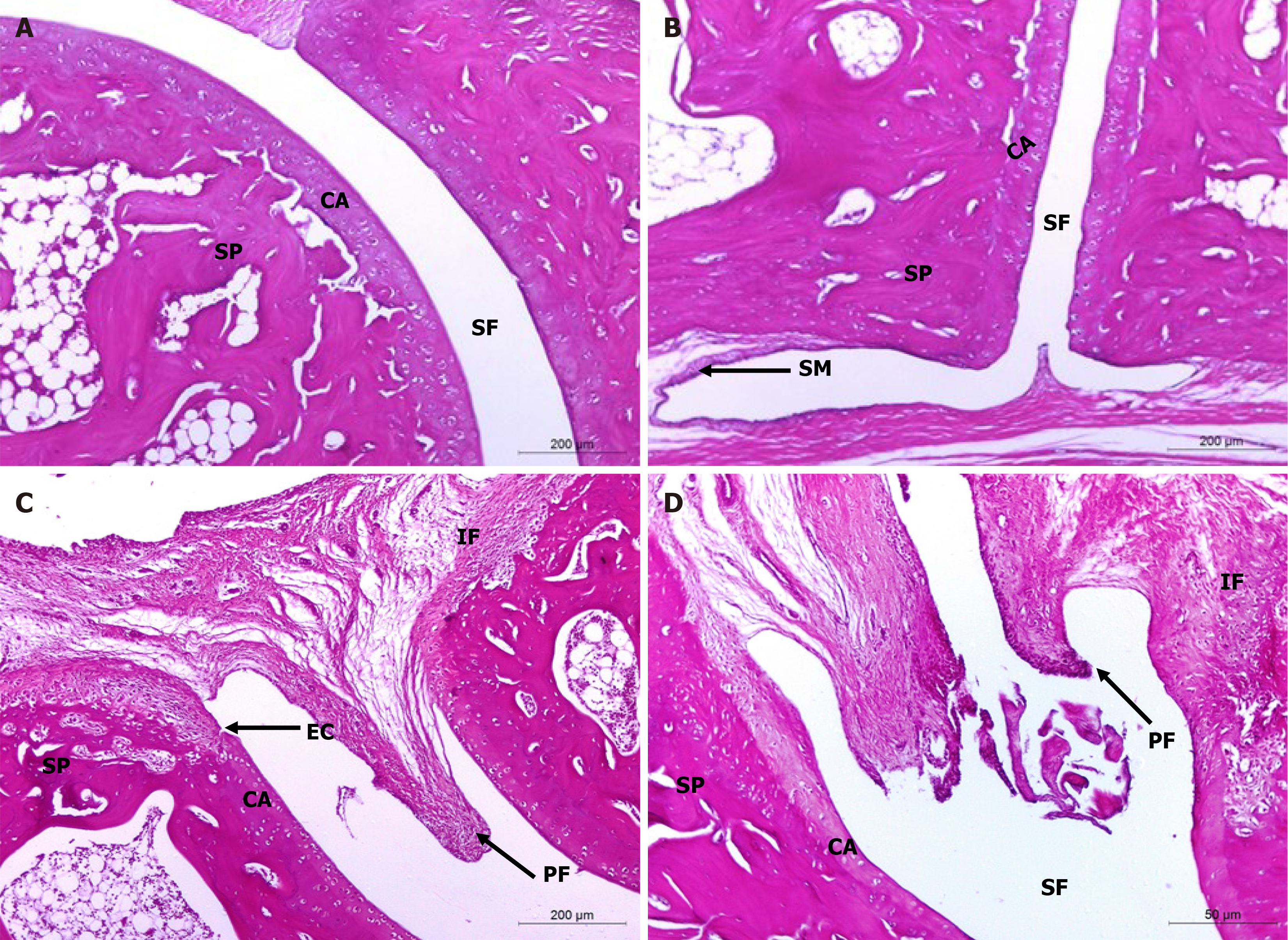
Figure 5 Histopathological evaluation of treatments on monosodium iodate-induced osteoarthritis in rat.
A and B: Microphotographs showing the histological changes in hind ankle of normal control (photomicrographs); C and D: Osteoarthritic control rats (photomicrographs) in Hematoxylin and eosin (100 ×) stained sections. The integral histological architecture of hind ankle joints was found in normal control rats. Osteoarthritic control rats showed synovial hyperplasia, mononuclear inflammatory cell infiltration, marked pannus formation, cartilage destruction and bone erosion. CA: Articular cartilage; EC: Erosion of cartilage; IF: Inflammatory cells infiltration; PF: Pannus formation; SF: Synovial fluid; SM: Synovial membrane; SP: Spongy bone.
- Citation: Hagag UI, Halfaya FM, Al-Muzafar HM, Al-Jameel SS, Amin KA, Abou El-Kheir W, Mahdi EA, Hassan GANR, Ahmed OM. Impacts of mesenchymal stem cells and hyaluronic acid on inflammatory indicators and antioxidant defense in experimental ankle osteoarthritis. World J Orthop 2024; 15(11): 1056-1074
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v15/i11/1056.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v15.i11.1056