Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Orthop. Apr 18, 2023; 14(4): 218-230
Published online Apr 18, 2023. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v14.i4.218
Published online Apr 18, 2023. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v14.i4.218
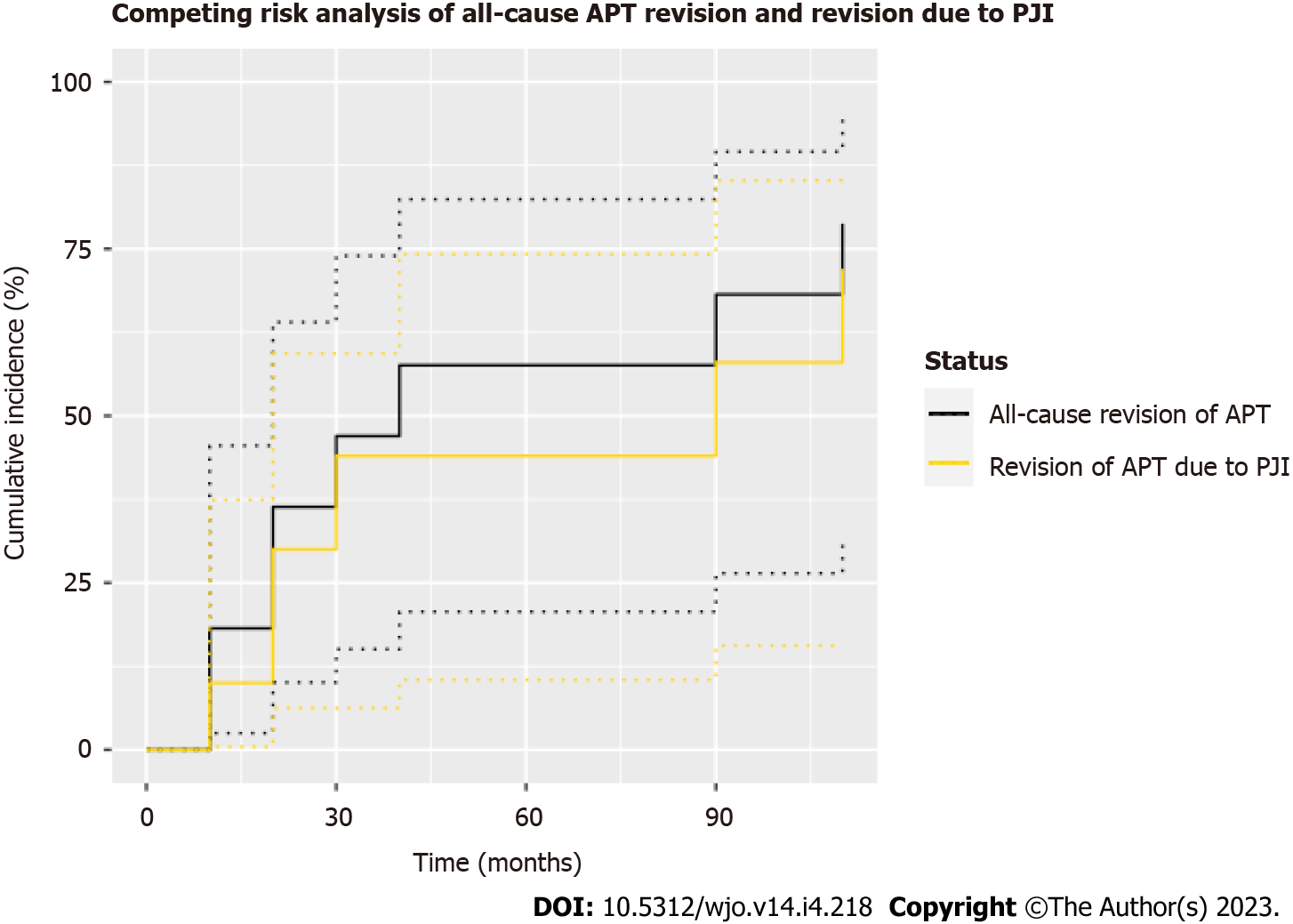
Figure 3 Competing risk analysis for cemented distal femoral replacement with all-polyethylene tibial components for oncologic indications with all-cause revision of the all-polyethylene tibial component (APT) and revision of the APT due to periprosthetic joint infection as the primary endpoints.
One- and three-year cumulative incidences were 18.2% (95%CI 2.5%-45.5%) and 47.0% (95%CI 15.1%-74.0%), respectively, with all-cause revision of the APT as the endpoint. One- and three-year cumulative incidences were 10.0% (95%CI 0.5%-37.4%) and 44.0% (95%CI 6.3%-59.3%), respectively, with revision of APT due to periprosthetic joint infection as the endpoint. APT: All-polyethylene tibial; PJI: Periprosthetic joint infection.
- Citation: Christ AB, Chung BC, Urness M, Mayer LW, Gettleman BS, Heckmann ND, Menendez LR. Clinical outcomes of cemented distal femur replacements with all-polyethylene tibial components for oncologic indications. World J Orthop 2023; 14(4): 218-230
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v14/i4/218.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v14.i4.218