Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Orthop. Mar 18, 2021; 12(3): 119-128
Published online Mar 18, 2021. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v12.i3.119
Published online Mar 18, 2021. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v12.i3.119
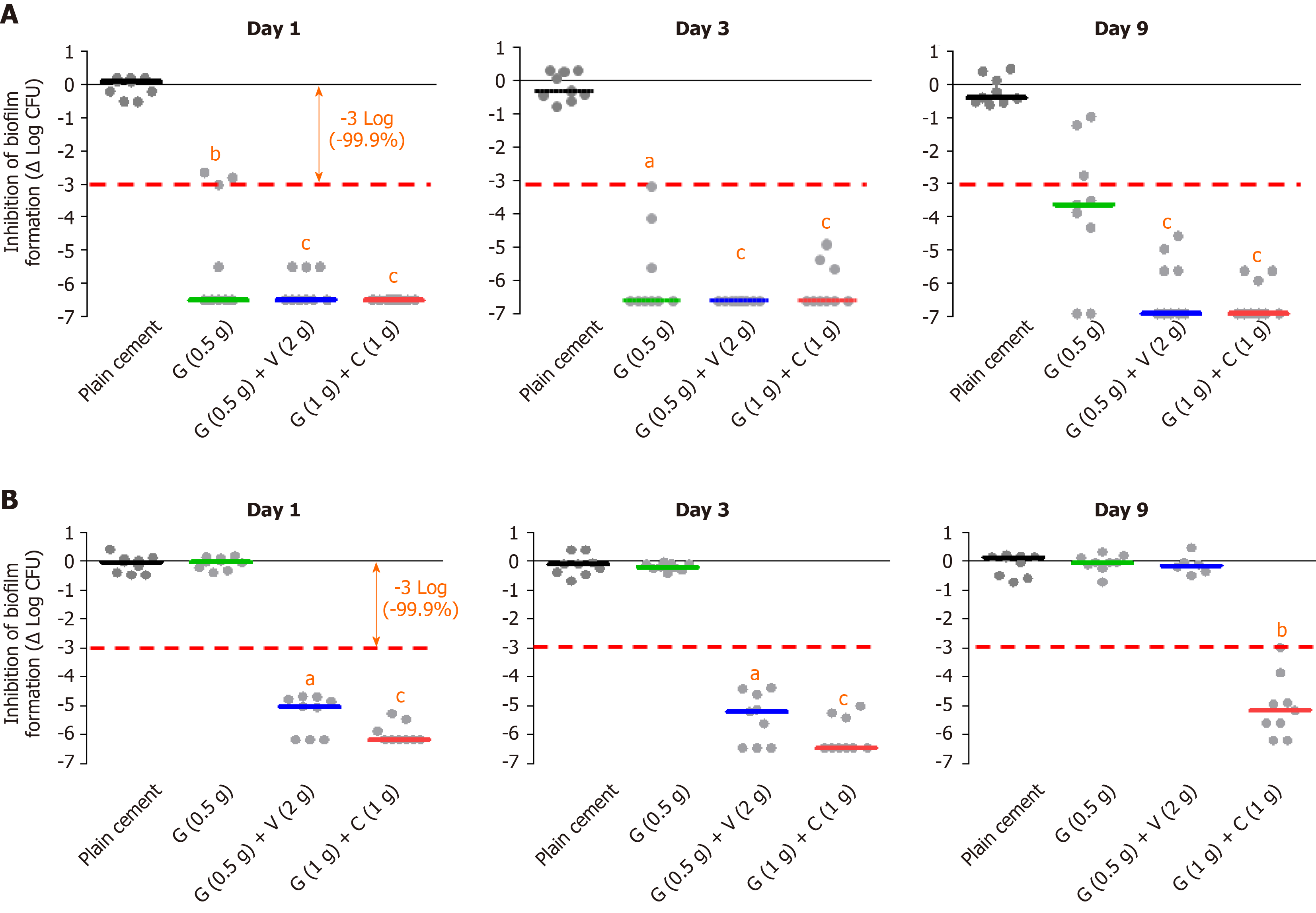
Figure 1 In vitro biofilm inhibition experiments with different bone cement types (plain, single and dual antibiotic-loaded bone cement).
A: Prophylactic anti-biofilm effect of three different antibiotic-loaded bone cements against a gentamicin and methicillin-susceptible Staphyloccus aureus strain at day 1, day 3 and day 9 on basis of three independent experiments; B: Prophylactic anti-biofilm effect of three different antibiotic-loaded bone cements against a gentamicin- and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis strain on basis of three independent experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, or cP < 0.001 respectively in comparison with PALACOS R (cement without antibiotic). G: Gentamicin; C: Clindamycin; V: Vancomycin.
- Citation: Berberich CE, Josse J, Laurent F, Ferry T. Dual antibiotic loaded bone cement in patients at high infection risks in arthroplasty: Rationale of use for prophylaxis and scientific evidence. World J Orthop 2021; 12(3): 119-128
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v12/i3/119.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v12.i3.119