Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Oncol. Aug 13, 2018; 9(4): 60-70
Published online Aug 13, 2018. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v9.i4.60
Published online Aug 13, 2018. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v9.i4.60
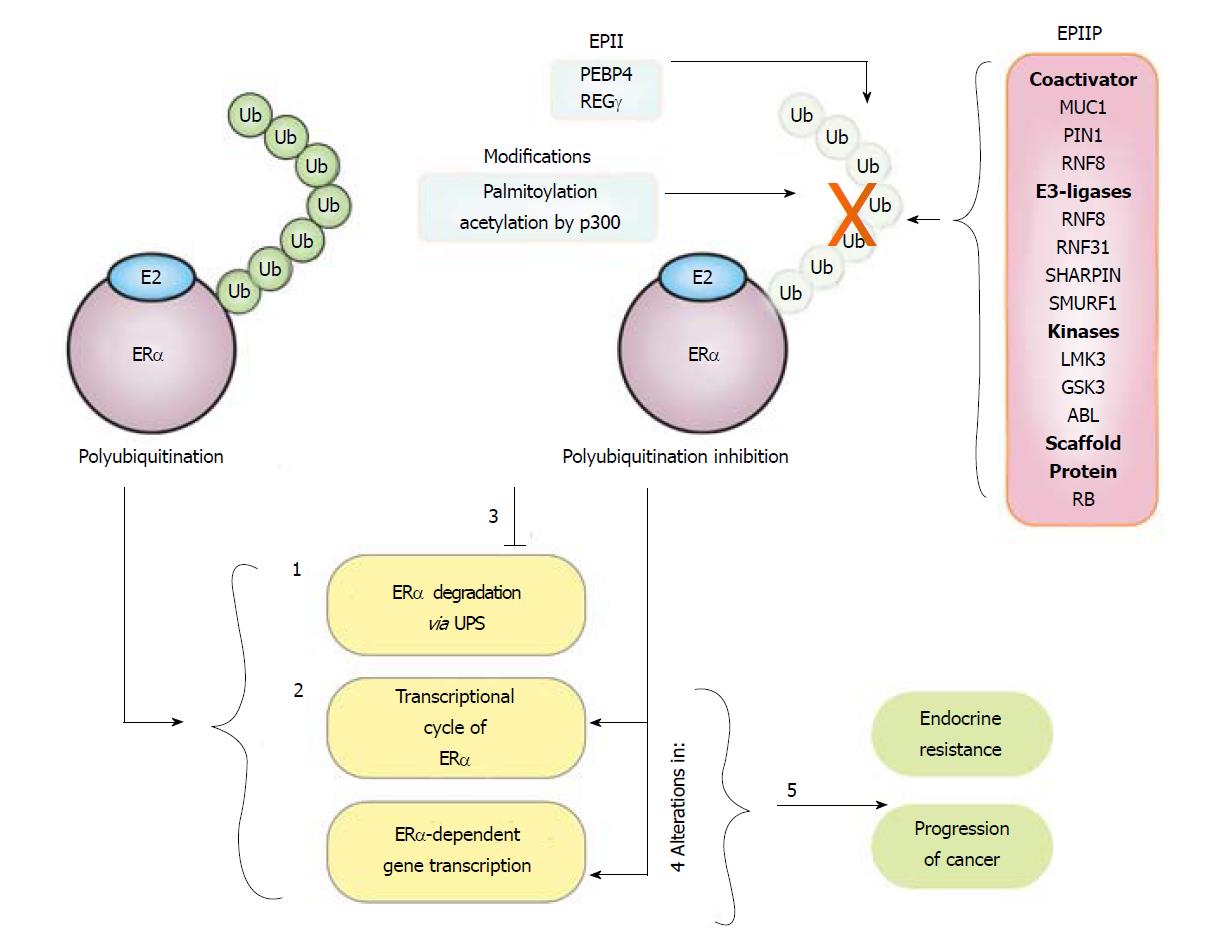
Figure 4 Mechanisms implicated in the estrogen receptor α polyubiquitination inhibition.
Half-life of estrogen receptor α protein oscillates between 3-5 h under basal condition. E2 treatment induces ERα polyubiquitination, and as result: (1) Degradation of this receptor is promoted, decreasing its protein levels starting from 1h after treatment; (2) the ERα transcriptional cycle is activated. ERα polyubiquitination inhibitor proteins (EPIP) and ERα polyubiquitination indirect inhibitors (EPII) and other modifications increased in breast cancer cells can inhibit the basal and E2-induced polyubiquitination of ERα; resulting in (3) the inhibition of its degradation and an enhancement in the ERα protein levels; (4) alterations in the transcription cycle of this receptor and the expression of its targets genes; and (5) these events seem to be associated with endocrine resistance and progression of breast cancer.
- Citation: Tecalco-Cruz AC, Ramírez-Jarquín JO. Polyubiquitination inhibition of estrogen receptor alpha and its implications in breast cancer. World J Clin Oncol 2018; 9(4): 60-70
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v9/i4/60.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v9.i4.60