Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Clin Oncol. Jun 10, 2016; 7(3): 308-320
Published online Jun 10, 2016. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v7.i3.308
Published online Jun 10, 2016. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v7.i3.308
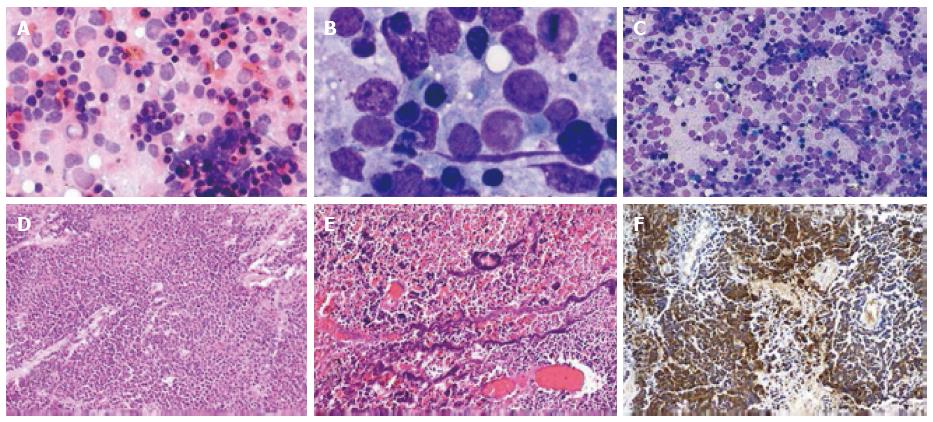
Figure 1 Histopathology and cytology of lymph node samples of illustrative case 1.
A: Microphotograph showing predominantly dispersed population of tumor cells (MGG × 20 ×); B: Microphotograph showing tumor cells with very high nuclear cytoplasmic ratio, scant cytoplasm, round nuclei and fine granular chromatin (MGG × 100 ×); C: Microphotograph showing tumor cells with many apoptotic bodies (HE × 40 ×); D: Photomicrographs showing clusters of tumour cells with small hyperchromatic nuclei, scanty cytoplasm and apoptosis; E: Photomicrographs showing Azzopardi phenomena (basophilic nuclear chromatin spreading to wall of blood vessels); F: Photomicrographs showing synaptophysin immunostain showing intense cytoplasmic positivity.
- Citation: Sehgal IS, Kaur H, Dhooria S, Bal A, Gupta N, Behera D, Singh N. Extrapulmonary small cell carcinoma of lymph node: Pooled analysis of all reported cases. World J Clin Oncol 2016; 7(3): 308-320
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v7/i3/308.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v7.i3.308