Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Clin Oncol. Dec 10, 2014; 5(5): 865-873
Published online Dec 10, 2014. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i5.865
Published online Dec 10, 2014. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i5.865
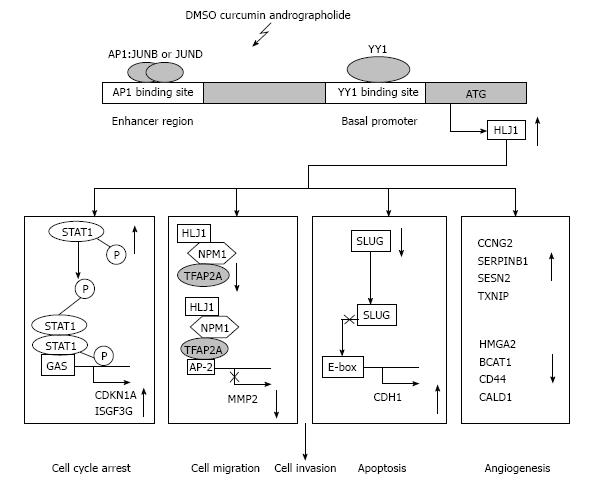
Figure 1 Schematic summary of the molecular mechanisms of HLJ1 in suppressing lung cancer tumourigenesis.
The endogenous transcriptional expression of HLJ1 is the result of the binding of the transcription factors AP1 and YY1 to the gene’s enhancer and promoter regions, respectively. HLJ1 inhibited lung cancer cell proliferation, anchorage-independent growth, cell motility, invasion and tumourigenesis through STAT1/p21WAF1 pathway, HLJ1/NPM1/AP2-α complex, SLUG/E-cadherin pathway and modulated cancer-related genes. DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide; AP1: Activating protein 1; GAS: Interferon-gamma activated sequence; CDKN1A: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A; YY1: Yin yang 1; STAT1: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; ISGF3G: Interferon-stimulated gene factor 3 gamma; NPM1: Nucleophosmin 1; TFAP2A: Transcription factor AP2 alpha; AP2: Activator protein 2; MMP2: Matrix metalloproteinase-2; SLUG: Snail homologue 2; CDH1: Cadherin 1; CCNG2: Cyclin G2; SERPINB1: Serine proteinase inhibitor B1; SESN2: Sestrin 2; TXNIP: Thioredoxin interacting protein; HMGA2: High-mobility group AT-hook 2; BCAT1: Branched-chain aminotransferase 1; CALD1: Caldesmon 1; E-box: E-box transcription factor binding site.
- Citation: Tsai MF, Wang CC, Chen JJ. Tumour suppressor HLJ1: A potential diagnostic, preventive and therapeutic target in non-small cell lung cancer. World J Clin Oncol 2014; 5(5): 865-873
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v5/i5/865.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v5.i5.865