Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Clin Oncol. Dec 10, 2014; 5(5): 1002-1019
Published online Dec 10, 2014. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i5.1002
Published online Dec 10, 2014. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i5.1002
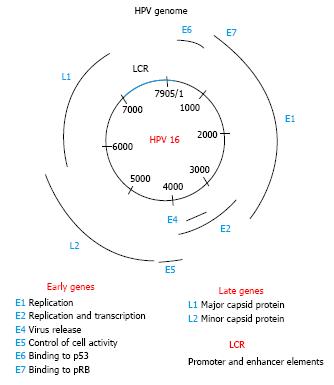
Figure 1 Human papilloma virus genome.
The genomic organization of the human papilloma virus 16 (HPV 16) is shown. The double strand DNA is close to 8000 base pairs. The early genes code for proteins involved in viral replication and transcription: E1, E2, E6, and E7 genes. The E4 and E5 genes are expressed a little later and have functions in immune evasion and virus release. The late genes code for the virus structural proteins: the major capsid protein L1, and the minor capsid protein L2. The E6 and E7 proteins of the high-risk HPV types have oncogenic properties. The long consensus repeat (LCR) sequence contains the promoter and enhancer elements of the virus.
- Citation: Rosales R, Rosales C. Immune therapy for human papillomaviruses-related cancers. World J Clin Oncol 2014; 5(5): 1002-1019
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v5/i5/1002.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v5.i5.1002