Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Clin Oncol. Jan 10, 2011; 2(1): 8-27
Published online Jan 10, 2011. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v2.i1.8
Published online Jan 10, 2011. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v2.i1.8
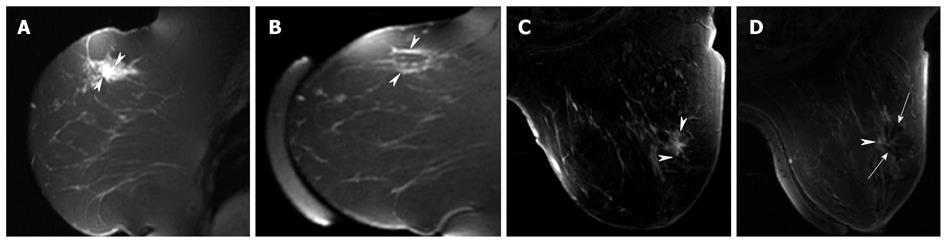
Figure 4 Sagittal contrast-enhanced T1-weighted fat-saturated magnetic resonance sagittal (A) and axial (C) images of a 1.
8-cm poorly differentiated invasive ductal carcinoma in a 44-year-old woman before MRgFUS. An irregular enhancing mass is seen in the upper outer quadrant of the right breast (arrow heads). Three days after magnetic resonance-guided focused US surgery (MRgFUS), minimal strikes of enhancement are seen without mass like enhancement in the sagittal image (arrow heads in B), which may represent hyperemia due to reactive inflammation or residual tumor. On the axial image (D), dark signal void area is seen at the site of the prior enhancing mass (long arrows). At histopathology, about 50% of the carcinoma and adjacent normal tissue showed thermal effects and the remaining portion of the carcinoma appeared viable.
- Citation: Zhou YF. High intensity focused ultrasound in clinical tumor ablation. World J Clin Oncol 2011; 2(1): 8-27
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v2/i1/8.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v2.i1.8