Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. Apr 24, 2025; 16(4): 104182
Published online Apr 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i4.104182
Published online Apr 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i4.104182
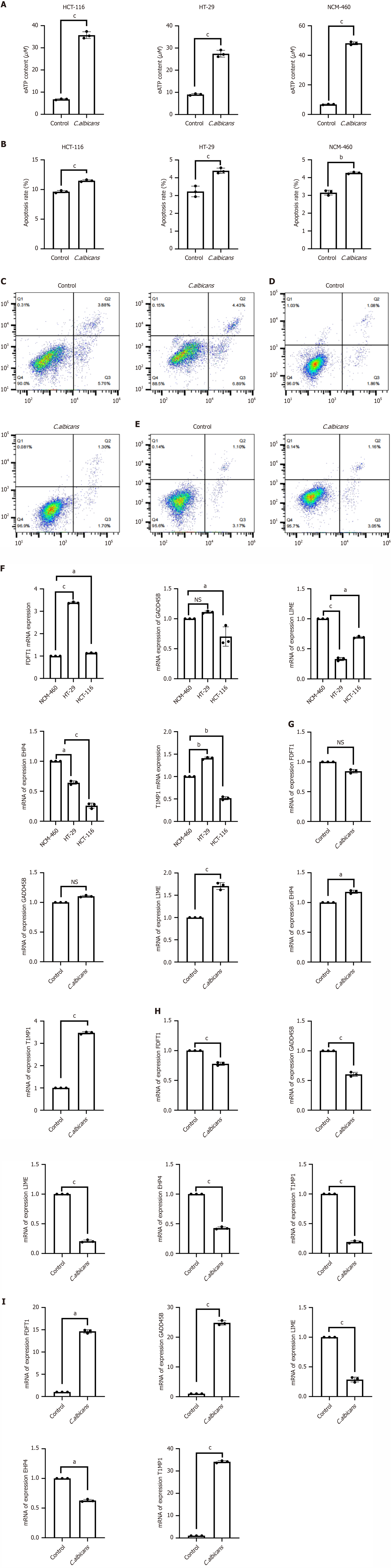
Figure 8 Candida albicans metabolic mixture interferes with extracellular ATP content, apoptosis and PCR detection of prognostic model gene expression in colorectal cancer cells.
A: Detection of extracellular ATP content; B: Histogram depicting cell apoptosis rates; C: Apoptosis rate in HCT-116 cells assessed via flow cytometry; D: Apoptosis rate in HT-29 cells detected by flow cytometry; E: Apoptosis rate in NCM-460 cells evaluated by flow cytometry; F: Expression levels of FDFT1, TIMP1, GADD45B, LIME1, and EHD4 across different cell types measured using real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR); G: RT-qPCR analysis of FDFT1, TIMP1, GADD45B, LIME1, and EHD4 expression in HCT116 cells treated with the Candida albicans (C. albicans) metabolite mixture; H: RT-qPCR analysis of FDFT1, TIMP1, GADD45B, LIME1, and EHD4 expression in HT29 cells treated with the C. albicans metabolite mixture; I: RT-qPCR analysis of FDFT1, TIMP1, GADD45B, LIME1, and EHD4 expression in NCM460 cells treated with the C. albicans metabolite mixture. (aP < 0.05,bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001).
- Citation: Zhang HL, Zhao R, Wang D, Mohd Sapudin SN, Yahaya BH, Harun MSR, Zhang ZW, Song ZJ, Liu YT, Doblin S, Lu P. Candida albicans and colorectal cancer: A paradoxical role revealed through metabolite profiling and prognostic modeling. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(4): 104182
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i4/104182.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i4.104182