Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. Apr 24, 2025; 16(4): 104061
Published online Apr 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i4.104061
Published online Apr 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i4.104061
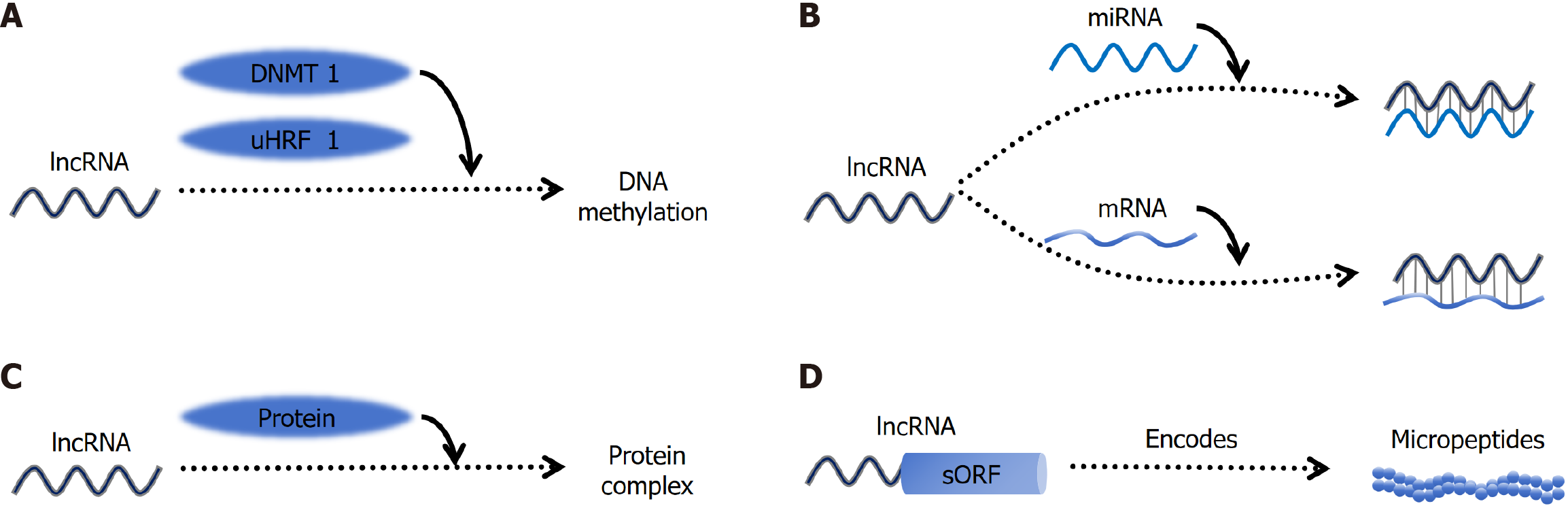
Figure 2 Functional mechanisms of long non-coding RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: UHRF1 drives hepatocellular carcinoma by inducing global DNA hypomethylation; B: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) bind to mRNAs and miRNAs to regulate their stability, thereby regulating gene expression; C: LncRNAs interact with proteins to regulate their stability or facilitate the formation of protein complex; D: Several lncRNAs hold the potential to encode small peptides, through which they exhibit their biological functions. lncRNAs: Long non-coding RNA.
- Citation: Wang J, Liu ZX, Huang ZH, Wen J, Rao ZZ. Long non-coding RNA in the regulation of cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(4): 104061
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i4/104061.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i4.104061