Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Oncol. Jan 24, 2024; 15(1): 130-144
Published online Jan 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i1.130
Published online Jan 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i1.130
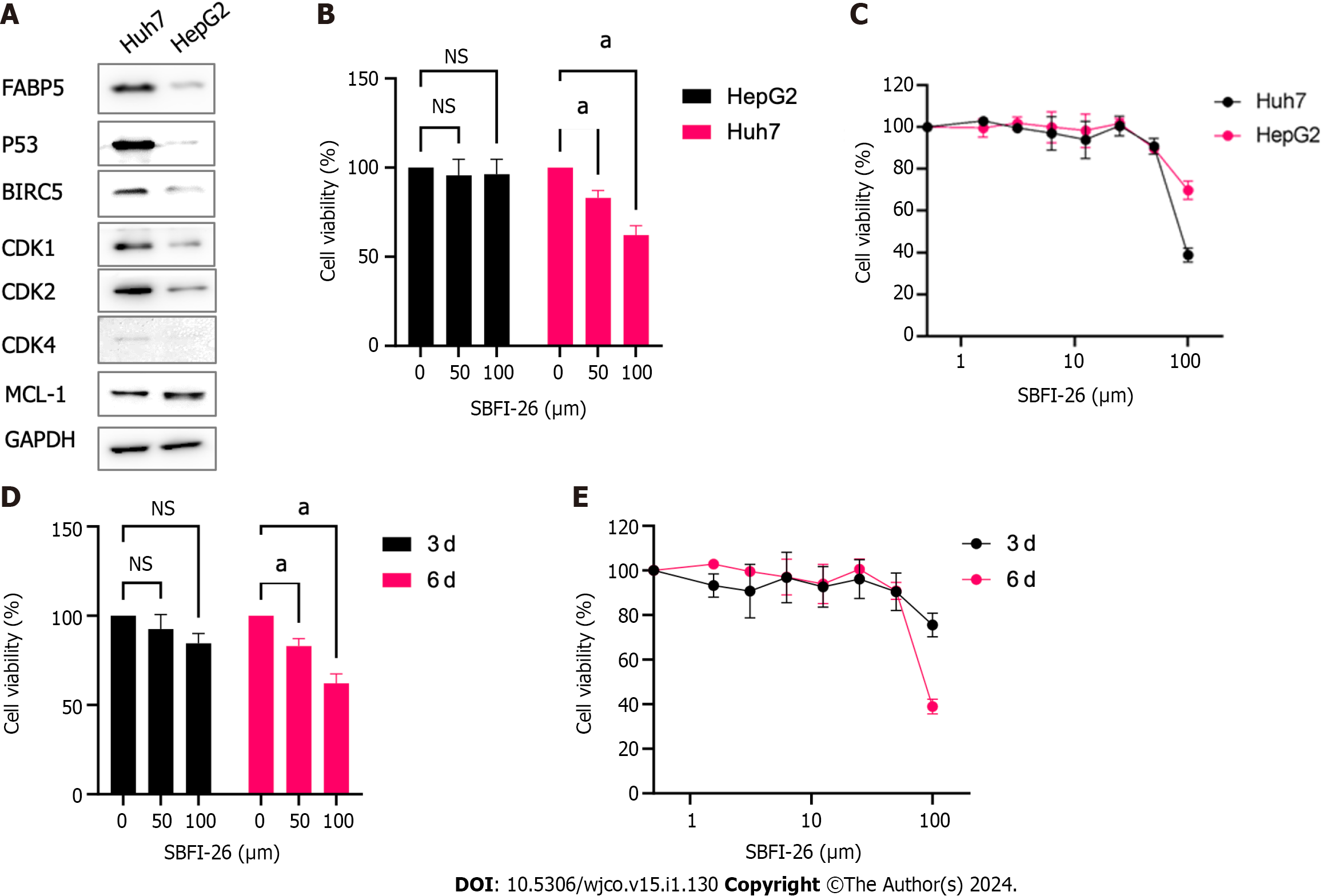
Figure 7 Huh7 cells are sensitive to FABP5 inhibition by SFBI-26.
A: Western blot shows the expression of FABP5, p53, and other proteins in Huh7 and HepG2 cells; B: 3-dose (0, 50 and 100 µmol/L) cell viability assay shows SBFI-26 inhibited the cell viability of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines Huh7 and HepG2 cells post treatment for 6 d; C: 8-dose (2-fold serial doses up to 100 µmol/L) cell viability assay showed SBFI-26 inhibited the cell viability of HCC cell lines post treatment for 6 d; D: 3-dose (0, 50 and 100 µmol/L) cell viability assay shows SBFI-26 inhibited the cell viability of Huh7 cells in time-dependent manner; E: 8-dose cell viability assay showed SBFI-26 inhibited the cell viability of Huh7 cells at 3- and 6-d post treatment; NS: Not significant.
- Citation: Li Y, Lee W, Zhao ZG, Liu Y, Cui H, Wang HY. Fatty acid binding protein 5 is a novel therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Clin Oncol 2024; 15(1): 130-144
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v15/i1/130.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v15.i1.130