Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Oncol. Dec 24, 2023; 14(12): 620-627
Published online Dec 24, 2023. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v14.i12.620
Published online Dec 24, 2023. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v14.i12.620
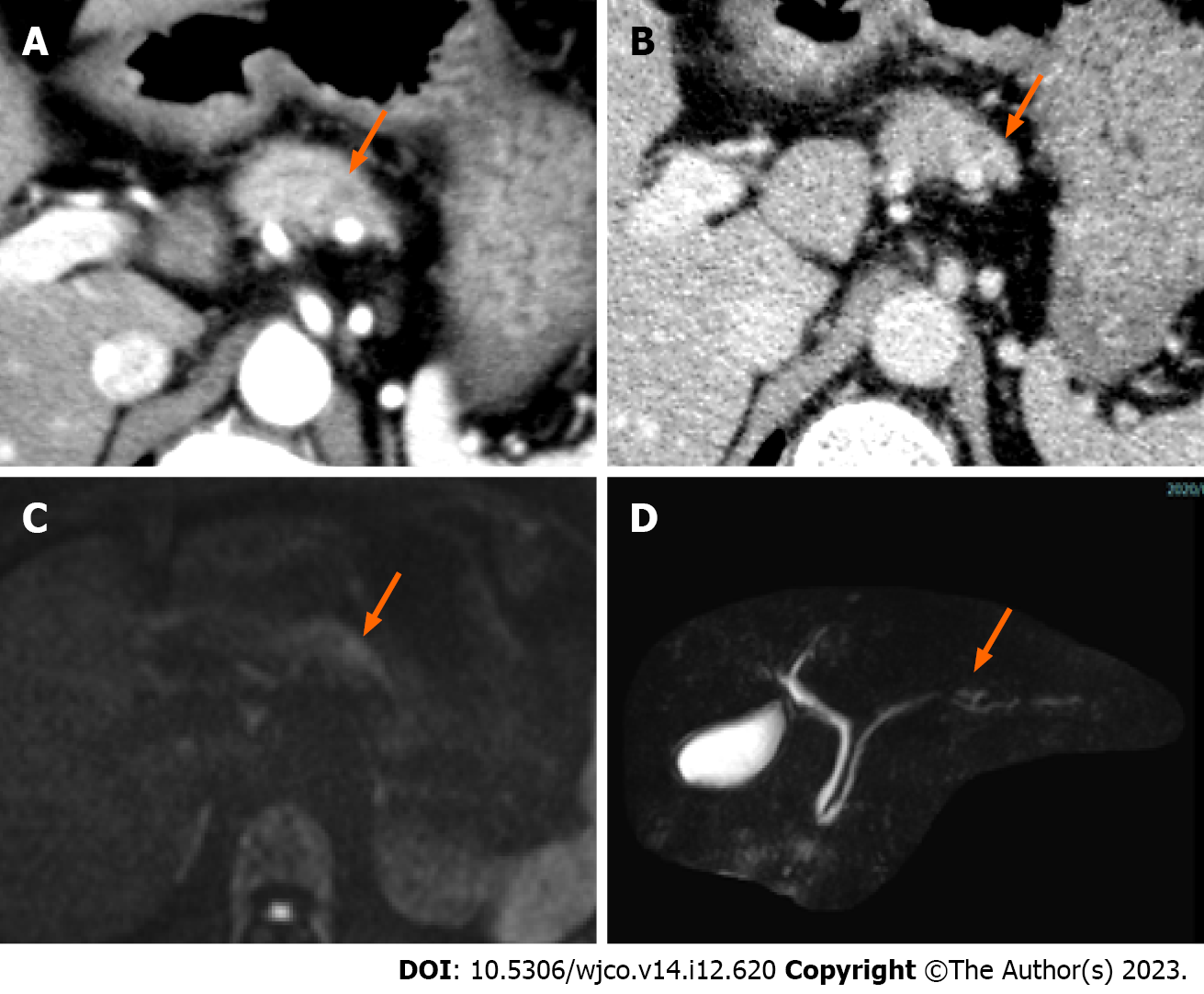
Figure 1 Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
A and B: A 5-mm nodule-like mass was observed in the pancreatic body; the nodule was not contrasted in the arterial phase, arrow (A) and was faintly contrasted in the late phase, arrow (B); C: Diffusion-weighted imaging showed a mild signal increase in the pancreatic body nodule noted on computed tomography, arrow; D: Magnetic resonance pancreatography showed no obvious dilatation or stenosis of the main pancreatic duct, arrow.
- Citation: Yamamoto K, Takada Y, Kobayashi T, Ito R, Ikeda Y, Ota S, Adachi K, Shimada Y, Hayashi M, Itani T, Asai S, Nakamura K. Rapid transformation of branched pancreatic duct-derived intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm into an invasive carcinoma: A case report. World J Clin Oncol 2023; 14(12): 620-627
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v14/i12/620.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v14.i12.620